Carding
Professional
- Messages
- 2,871
- Reaction score
- 2,467
- Points
- 113
With the adoption of Federal Law No. 167-FZ of June 27, 2018 "On Amendments to Certain Legislative Acts of the Russian Federation Regarding Anti-Theft of Funds" and the increasing number of attacks on banking systems, interest in anti-fraud systems in the banking sector (antifraud) and detection of attempts to commit fraudulent transactions in remote banking systems (RBS). Such systems allow detecting and preventing fraudulent activities using machine learning technologies, digital profiles of devices and users, etc.
1. Introduction
1. The global market for anti-bank fraud systems
3. The market for anti-banking fraud systems in Russia
4. Functions of anti-bank fraud systems
5. A Brief Overview of Anti-Bank Fraud Systems
5.1. Comprehensive banking fraud and anomaly detection systems
5.1.1. ARIC White Label
5.1.2. FICO Application Fraud Manager
5.1.3. FraudWall
5.1.4. FRAUD-Analysis
5.1.5. IBM Safer Payments
5.1.6. Intellinx
5.1.7. Jet detective
5.1.8. Nice actimize
5.1.9. SAS Fraud and Security Intelligence
5.1.10. Smart Fraud Detection
5.2. Systems for identifying banking fraud instruments
5.2.1. Threat detector
5.2.2. Digital Banking Fraud Detection
5.2.3. F5 WebSafe
5.2.4. IBM Trusteer Rapport
5.2.5. Kaspersky Fraud Prevention
5.2.6. ThreatMetrix
5.2.7. Group-IB Secure Bank
5.2.8. WEB ANTIFRAUD
5.3. Highly specialized systems for detecting signs of banking fraud
5.3.1. FPS.Bio
5.3.2. SmartTracker.FRAUD
5.4. Mixed anti-bank fraud systems
5.4.1. RSA Adaptive Authentication and Transaction Monitoring
5.4.2. BI.ZONE Cloud Fraud Prevention
6. Findings
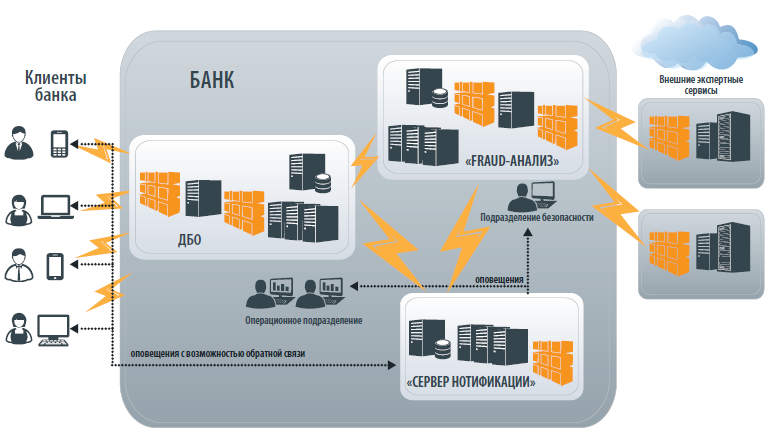
Introduction
Since many banking and payment transactions have moved into the field of informatization, fraud in this area has been actively developing. The most famous attacks on banking systems in the past few years have been carried out by the criminal gangs Cobalt, Carbanak, Lazarus and Lurk. According to Sberbank's estimates, Russia's losses from cyberattacks amount to about 650 billion rubles a year. At the same time, in the first two weeks of 2019 alone, Sberbank was subjected to 18 cyber attacks. Cybercriminals carry out attacks on interbank transfer systems, card processing, ATM management, Internet banking and payment gateways.
According to the Positive Technologies report, attackers use a simple attack scenario that consists of 5 sequential stages:
1. Preliminary exploration and preparatory work.
2. Penetration into the internal network.
3. Anchoring in the internal network and developing the attack.
4. Compromise of banking systems and theft of funds.
5. Hiding traces.
These stages are relevant when phishing, infecting a victim's computer or smartphone with previously known malware, conducting man-in-the-middle attacks, using keyloggers and even zero-day vulnerabilities.
Group-IB specialists identified 7 common schemes of theft of funds during attacks on remote banking systems (RBS):
The global market for anti-bank fraud systems
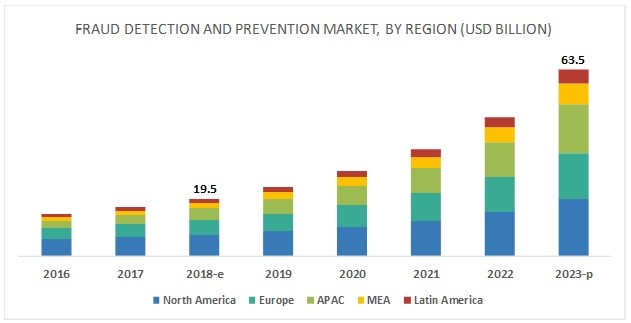
In 2020, the global market for anti-fraud systems was valued at US $ 13.59 billion. The scale is projected to reach $ 31.15 billion (CAGR = 16.42%) for 2024. This is due to the increased opportunities for fraud due to the increase in the number of transactions (both monetary and information-oriented), technological advances, as well as the general digitalization of the financial sector.
Figure 1. Market size of antifraud systems in the world by region (North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, Central Asia and Africa, Latin America)
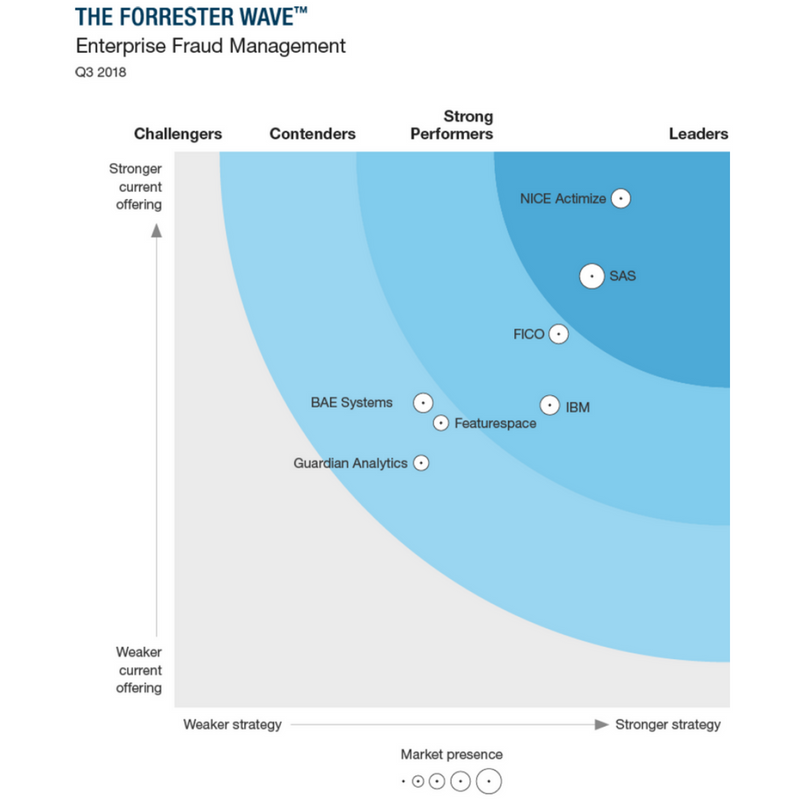
According to Markets and Markets reports, the following companies are the main providers of anti-banking fraud systems around the world:
Figure 2. Rating of anti-fraud systems developers, according to The Forrester Wave
The market for anti-banking fraud systems in Russia
The antifraud systems market in Russia has gone through several characteristic stages of development. Evolutionary breakthroughs were such important milestones as the emergence of Chip Liability Shift in 2007-2008, and before that the emergence of a standard for monitoring bank card transactions from Visa in 2003, which gave impetus to the components of antifraud systems in processing. In 2011-2012. there was a massive series of attacks on remote banking systems, initially affecting mainly legal entities and subsequently spreading to citizens. In 2014-2015. banking Trojan Lurk and other malicious programs gave impetus to the emergence of Russian solutions from Group-IB and Kaspersky Lab. In 2018, the adopted Federal Law of June 27, 2018 No. 167-FZ "On Amendments to Certain Legislative Acts of the Russian Federation Regarding Countering the Theft of Funds" again heated the issue of anti-fraud systems, especially for those representatives of the credit and financial sector, for whom the acts of implementation of transactional fraud were small and in fact measured below the cost of the anti-fraud solutions themselves. According to Sberbank, in 2018, with the help of the introduced anti-fraud system, it was possible to save more than 32 billion rubles belonging to depositors.
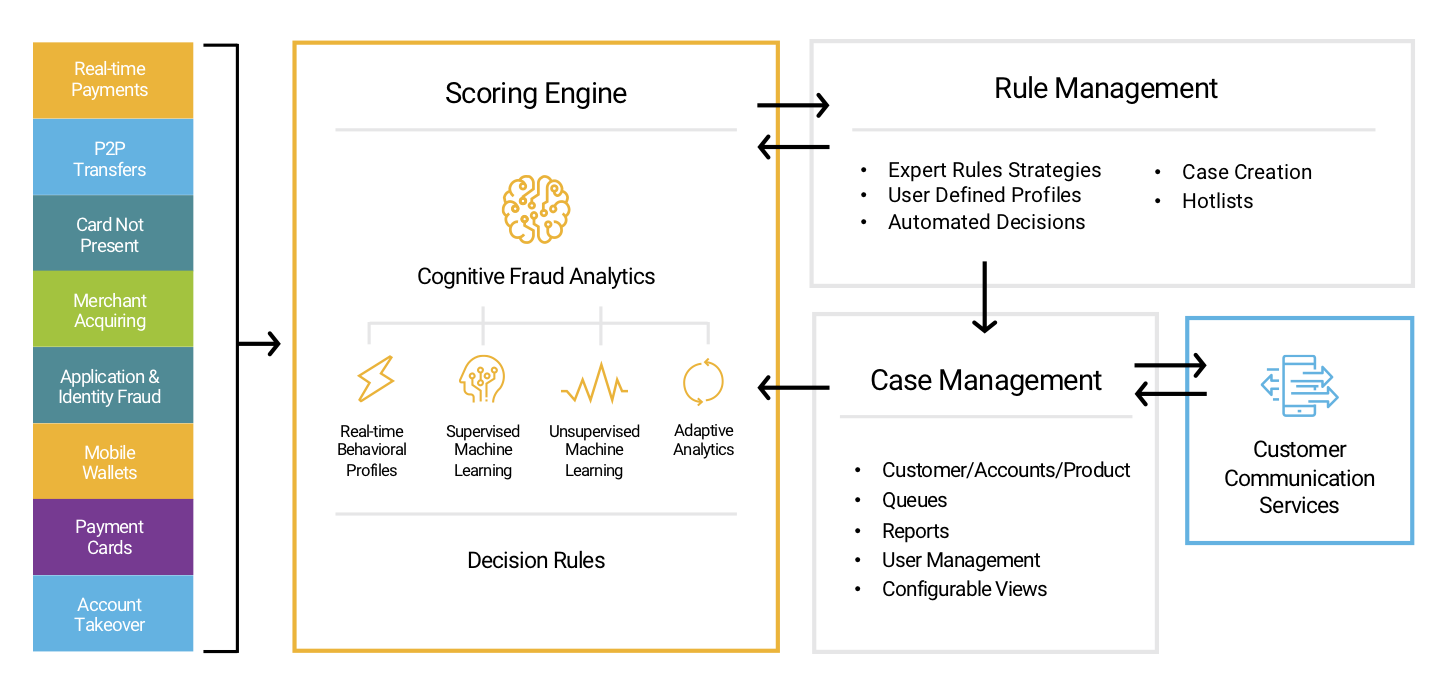
Functions of anti-bank fraud systems
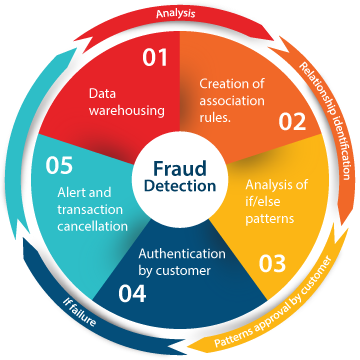
The fraud detection and prevention process does not have an initial or final stage, it must be carried out continuously and include the following sub-processes:
Monitoring;
Detection;
Making decisions;
Training.
Figure 3. The principle of operation of anti-fraud systems
Anti-fraud systems can have the following technologies and capabilities in their arsenal:
All anti-fraud systems have the same function - to detect and prevent fraud. However, they can solve this problem in different ways and compare anti-fraud systems without additional classification is a wrong decision.
So, for example, there are so-called core-systems - powerful analytical platforms that allow you to implement logic in separate segments (RBS or bank card processing), there are also specialized systems that control the parameters of devices and risks on their side. And at the same time, separate systems are being developed, sharpened for the recognition of photo, video, speech. Many of the systems do not compete, but, on the contrary, complement each other's functions. For example, a specific highly specialized solution cannot by itself cover the requirements of the Federal Law of 27.06.
Based on this, we have divided the existing systems for combating banking fraud into 3 classes:
1 class. Solutions of this class are aimed at detecting and identifying traces of fraud and detecting anomalies.
2 class. Solutions of this class are aimed at identifying fraud tools, cause or risk (for example, the presence of malware, remote control components, phishing components).
3 class. Solutions of this class solve highly specialized tasks. In particular, they can be designed for image recognition to detect fraud, and can be equipped with a speech recognition system.
A Brief Overview of Anti-Bank Fraud Systems
Comprehensive banking fraud and anomaly detection systems.
ARIC White Label
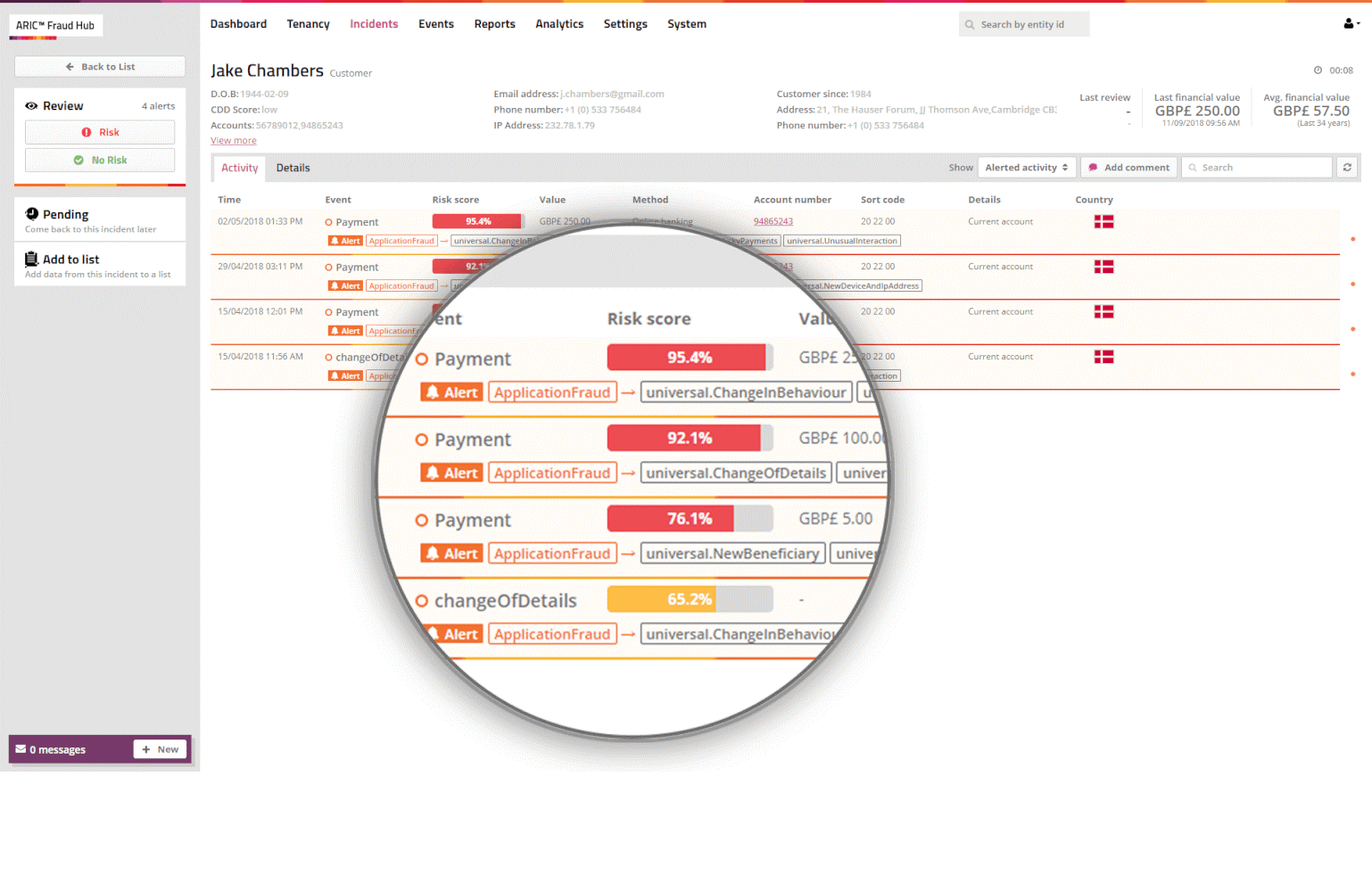
Featurespace was founded in 2008 (Cambridge, UK). The company was founded by a professor at the University of Cambridge with the goal of developing an adaptive behavioral analytics engine that enables fraud protection based on anomaly detection. Featurespace's ARIC White Label system belongs to the class of general analytical platforms. The system uses machine learning technologies to provide protection against fraudulent transactions for various types of payments (cards, e-wallets, etc.) in real time. In ARIC White Label, models of normal customer behavior are created, deviations in which are subsequently recorded by the system. Different analysis rules can be created for different clients, they can also be given access to the ARIC White Label to set up their own rules and models for work.
Figure 4. ARIC White Label system interface
Features of ARIC White Label:
FICO Application Fraud Manager
FICO was founded in 1956 (San Jose, California, USA). The company specializes in the development of predictive analytics and decision making software, including solutions for assessing credit risks, as well as reducing losses from fraudulent activities.
The FICO Application Fraud Manager system from FICO belongs to a general analytical platform and real-time identification of fraud attempts through an analytical system that uses machine learning and adaptive analysis technologies. The solution can be installed both locally and used using SaaS technology. The system allows you to prevent fraudulent attempts by third parties, as well as attempts to deliberately abuse account privileges aimed at fraud with credit and debit payment cards, electronic payments, and deposit accounts.
Figure 5. Diagram of the FICO Application Fraud Manager system
Features of FICO Application Fraud Manager:
FraudWall
The Frodeks company was founded in 2011 (Ufa). The company specializes in information security services, development and implementation of intelligent systems for detecting fraudulent payments, data processing systems, and information security investigations. Frodex's flagship solution is FraudWall, a fraudulent payment detection system, which has been assigned a class of information systems for solving specific industry problems. The FraudWall system from the Frodex company can be classified as a general analytical platform. It is designed to prevent theft of client funds in remote banking systems (RBS), to combat internal fraud (for example, unauthorized payments in the ABS), to prevent the theft of bank funds through the AWS KBR. When the system detects a suspicious payment, it makes a call to the client and conducts live communication with him, recognizing the client's responses. Upon completion of the call, FraudWall decides to execute the payment or stop the operation.
Figure 6. FraudWall system interface
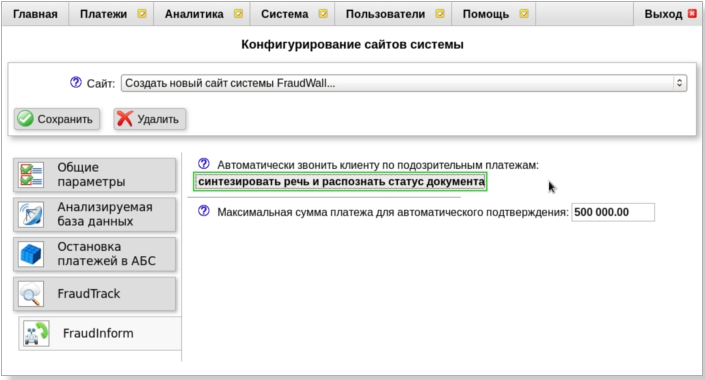
FraudWall features:
FRAUD-Analysis
Bank Software Systems (BSS) was founded in 1994 (Moscow). The main direction of the company is the development and implementation of automated systems for remote banking and financial management. In addition to complex systems for the financial market, BSS develops specialized products, including FRAUD-Analysis. The FRAUD-Analysis system from BSS can be classified as a general analytical platform, but the system is designed primarily to prevent fraud when servicing individuals and legal entities by the bank within the framework of BSS's own solutions. FRAUD analysis is capable of protecting against threats of using stolen authentication means and the private key of an electronic signature, threats of access to an open session of working with the system, threats of altering payment document details (for example, using malware).
Figure 8. Diagram of the FRAUD-Analysis system
Features of FRAUD-Analysis:
IBM Safer Payments
IBM was founded in 1911 (Armonk, New York, USA). The company is one of the world's largest manufacturers and suppliers of hardware and software, IT services and consulting services. The company has a subsidiary Trusteer, which deals with computer security, including the development of anti-fraud systems. The IBM Safer Payments solution from IBM is a common analytics platform. It is developed on the IRIS platform following the IBM acquisition of IRIS Analytics. The system is designed to detect fraud attempts in real time. At the same time, security is ensured both when making non-cash payments in many systems (automated clearing houses, acquiring banks, the Single Euro Payments Area, Chip & Pin and others), and through merchant terminals, ATMs, online and mobile banks.
Figure 8. IBM Safer Payments system interface
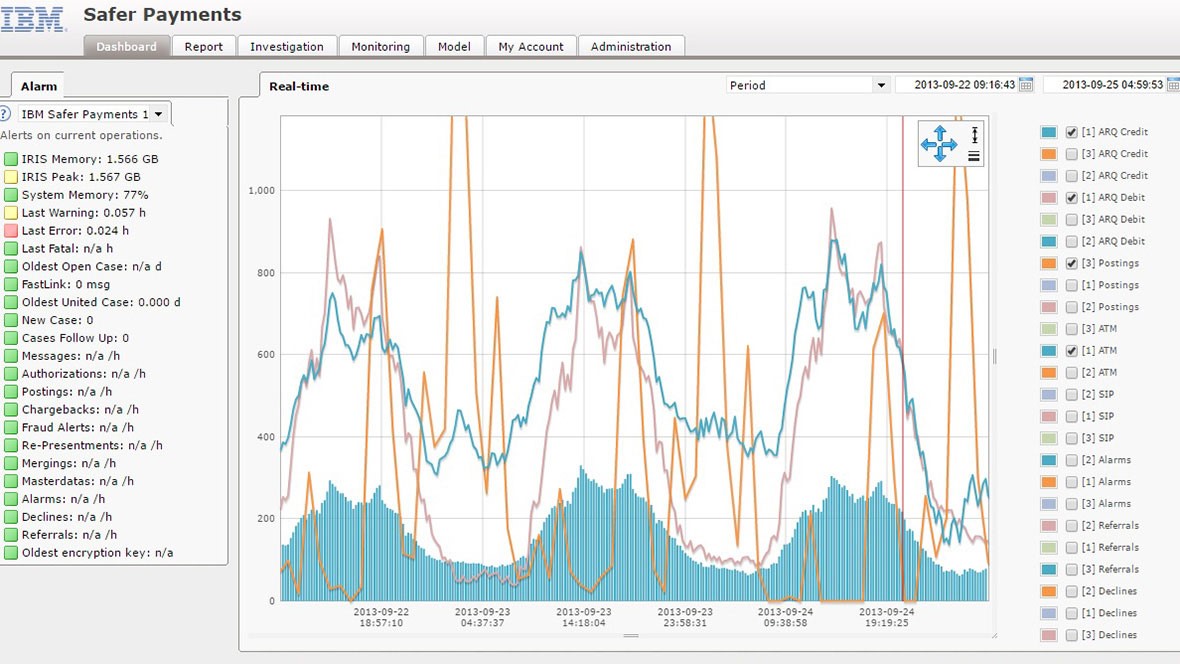
Features of IBM Safer Payments:
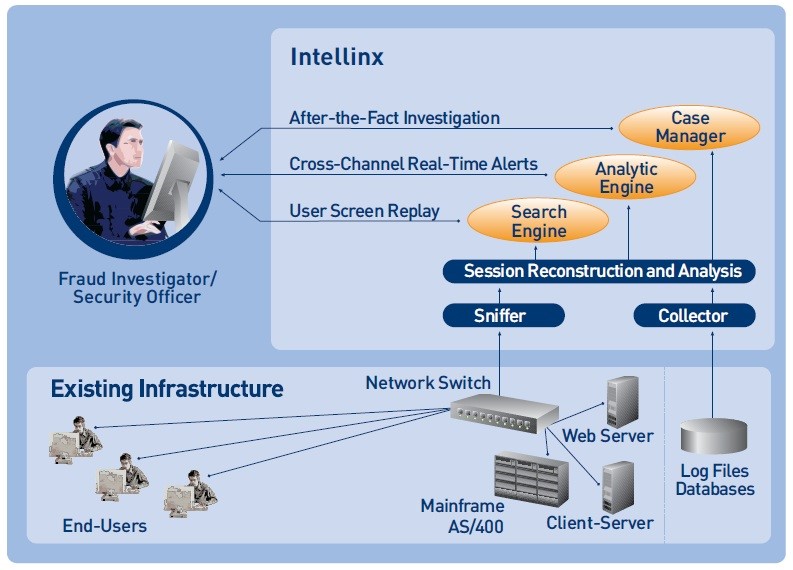
Intellinx
Intellinx Ltd. founded in 2005 (Or Yehuda, Israel). The company develops solutions for tracking end-user activities and preventing data leaks from organizations. At the same time, the means of protection are aimed at protecting both from outside violators and from employees of organizations. Intellinx solution from Intellinx Ltd. belongs to the class of general analytical platforms. The system enables compliance with regulatory requirements such as Basel II, STO BR IBBS and others by detecting identity theft attempts and other types of fraud in Internet banking and other online services. At the same time, Intellinx can track the activity of system administrators and other privileged users, monitor availability and response time in critical processes. The system can track cases of compromised PIN codes, as well as attempts to carry out transactions on the same account from different locations in a short period of time.
Figure 9. Diagram of the Intellinx system
Intellinx features:
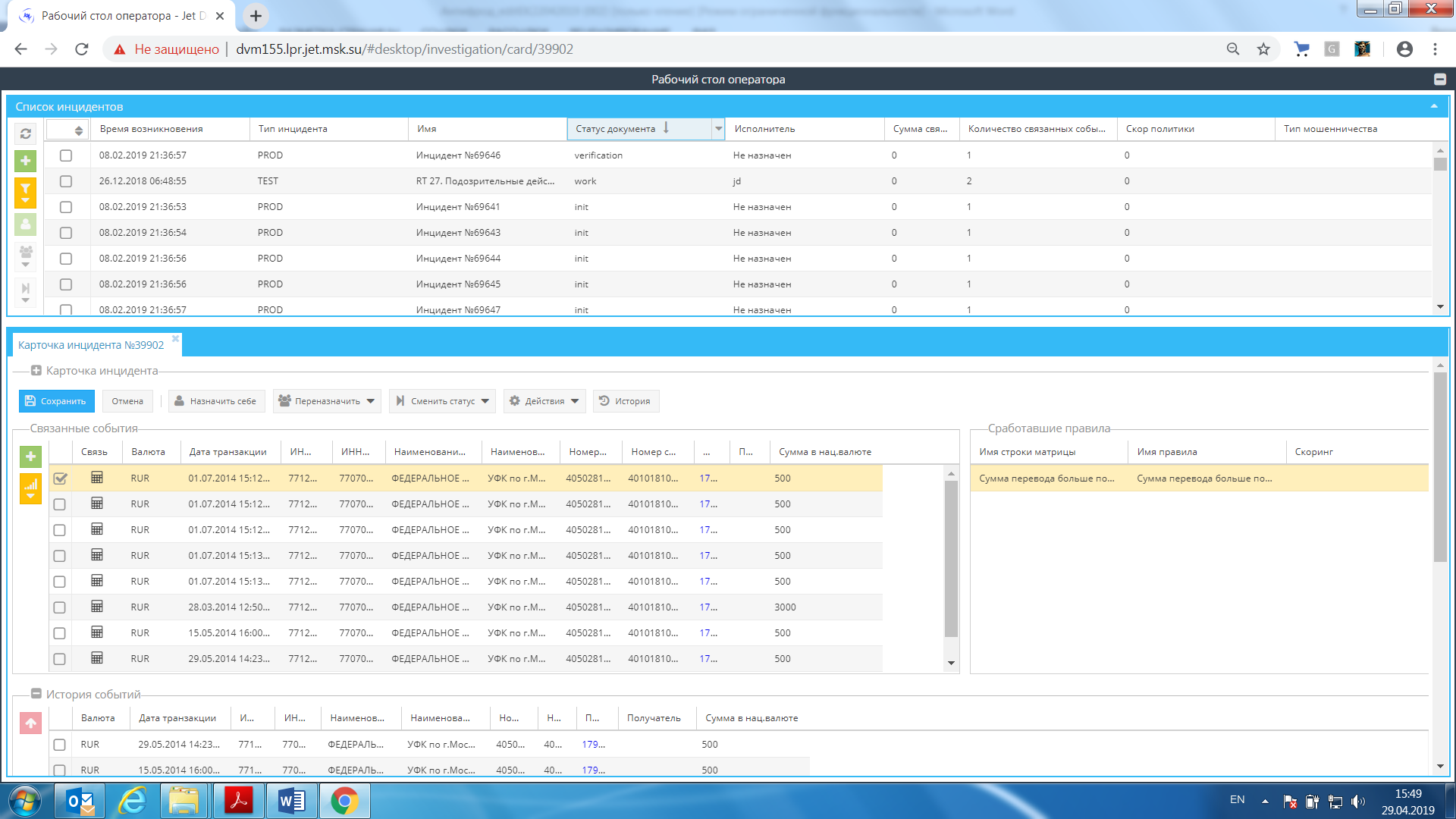
Jet detective
Jet Infosystems was founded in 1991 (Moscow). One of the directions of the company is information security and development of solutions to ensure the security of commercial and government organizations. Jet Infosystems specializes in the construction of integrated security systems, protection of cloud infrastructure, incident management, as well as anti-fraud and income guarantee systems in the banking and telecommunications sectors, retail, as well as in the fuel and energy complex. Jet Detective antifraud system from Jet Infosystems is a general analytical cross-channel platform and performs such functions as countering internal and third-party fraud, monitoring business processes, behavioral analytics for employees, customers and business systems, as well as checking for compliance with requirements. The application is developed in accordance with a three-tier architecture - client, application server and data storage layer - and consists of 6 functional modules (Desktop, Data Factory, Event Analysis, Incident Investigation, Machine Learning, Authorization). The product fully complies with the current requirements of the legislation of the Russian Federation on combating fraud and ensuring AML / CFT.
Figure 10. Jet Detective System Interface
Features of Jet Detective:
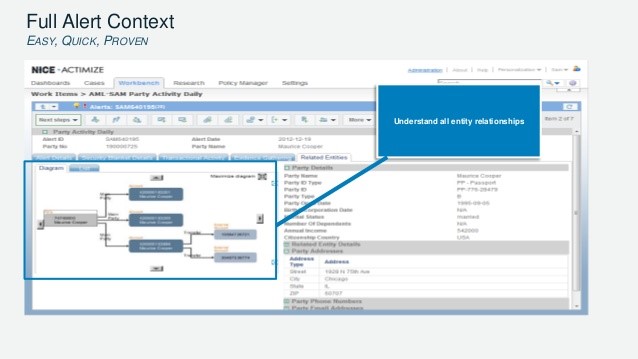
Nice actimize
NICE Systems Ltd. founded in 1986 (Ra'anana, Israel). The company develops both cloud-based and on-premise software to improve customer experience for businesses, comply with regulations, and prevent financial crime. Nice Actimize solution from NICE Systems Ltd. belongs to the class of general analytic platforms and allows detecting, preventing and investigating cases of money laundering through built-in AML lifecycle management and fraud in real time. The system provides protection for all types of payments, including SWIFT / Wire, Faster Payments, BACS SEPA payments, ATM / debit transactions, bulk payments, invoice payments, P2P / postal payments and various forms of internal transfers available in various markets.
Figure 11. Nice Actimize system interface
Nice Actimize Features:
SAS Fraud and Security Intelligence
SAS was founded in 1976 (Cary, North Carolina, USA). The company is a large private IT company in the world and specializes in the development of technological software and applications of the Business Intelligence, Data Quality and Business Analytics classes. SAS has developed a comprehensive SAS Fraud and Security Intelligence (SAS FSI) solution that provides a unified platform for addressing the challenges of preventing transactional, credit, internal and other types of fraud. The SAS FSI solution belongs to the class of high-performance cross-channel platforms and is capable of processing thousands of transactions per second. It combines fine-tuning of business rules with machine learning technologies to prevent fraud with minimal positives. The investigation interface allows you to reveal hidden relationships between payment participants, and is also fully customizable to the needs of users. The block for working with machine learning models in the SAS system allows an ordinary user, without programming skills, to create a model and apply it to the transaction flow.
Figure 12. SAS FSI Component Interface
Features of SAS Fraud Management:
Smart Fraud Detection
Fuzzy Logic Labs has been developing, implementing and supporting software in the field of banking antifraud since 2011. Smart Fraud Detection system is designed to counter fraudulent transactions in various customer service channels: RBS for retail and corporate business; mobile and SMS bank; processing of plastic cards (emission); payment terminals, acquiring, internet acquiring; operations and calls through IVR and call center employees; actions and operations of bank employees in the office; operations using instant messengers and chat bots.
Figure 13. Scheme of the Smart Fraud Detection system
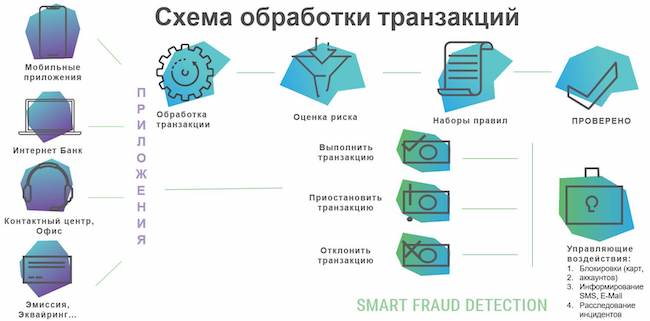
The Smart Fraud Detection system can solve tasks for three classes of fraud monitoring in banks. The system checks payments in real time, builds operator and client profiles, recognizes employee behavior using cameras and microphones, monitors transaction dependencies in different business areas and in different systems of the bank's IT architecture. The main activity of the company is combating external and internal fraud, as well as money laundering.
Figure 14. Incident card in the Smart Fraud Detection system interface
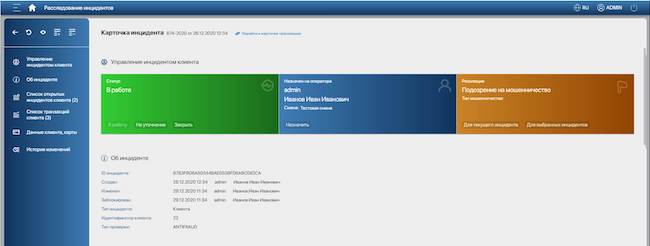
Features of the Smart Fraud Detection system:
Systems for identifying banking fraud instruments
Threat detector
The BIFIT company (Banking and financial Internet technologies) was founded in 1999 (Moscow). The company specializes in the development of complex platforms for remote banking services, including for entrepreneurs, organizations, holdings and individuals. A feature of Internet banking systems from the BIFIT company is the use of Java technology, which makes it possible to expand the list of supported operating systems and client browsers. The "Threat Detector" module for protection against fraud of the BIFIT company is built into the iBank 2 system, which is designed to provide bank customers with services for remote account management. The general capabilities of the security subsystem include the use of an electronic signature mechanism, the use of cryptographic data transformation during transmission between the client and the bank, as well as the use of a cryptographic authentication mechanism of the parties. The built-in Threat Detector module allows you to detect malicious programs on a client's computer designed for theft in an RBS environment. At the same time, the security administrator has access to the ability to view information about infected workplaces of clients, the ability to analyze documents with which work was carried out on these workstations,
Figure 15. Threat Detector system interface
Features of iBank 2:
Digital Banking Fraud Detection
Guardian Analytics was founded in 2005 (Mountain View, California, USA). The main focus of the company is the development of fraud prevention systems for financial institutions. The Digital Banking Fraud Detection system from Guardian Analytics belongs to the general analytical platforms. Like other fraud prevention systems, the system can be implemented both locally and as a cloud service. At the same time, Digital Banking Fraud Detection protects against attempts to hijack a client's account, fraudulent transfers, phishing and attacks like MITB in real time. A profile is created for each user, on the basis of which anomalous behavior is recognized.
Figure 16. Interface of Digital Banking Fraud Detection system
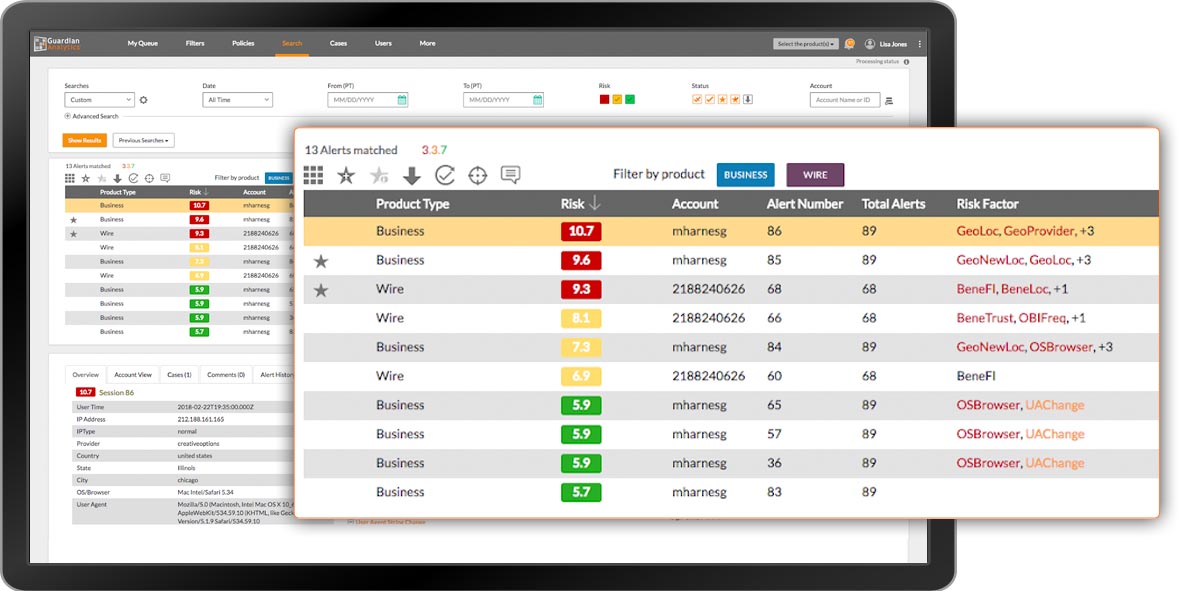
Features of Digital Banking Fraud Detection:
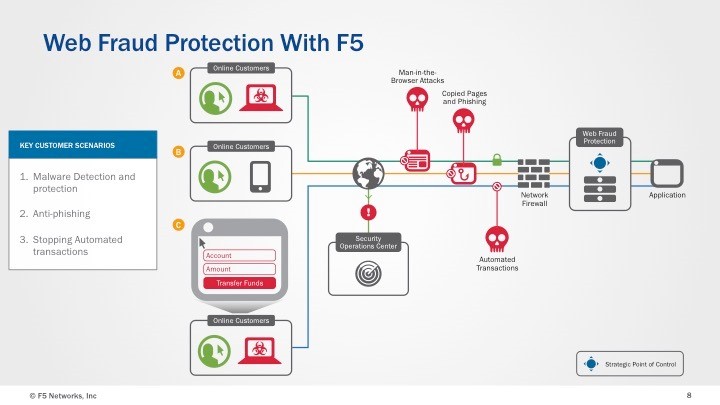
F5 WebSafe F5 was founded in 1996 (Seattle, Washington, USA). The company develops information security systems, including Web Application Layer Firewalls (WAFs), DDoS protection systems, Next Generation Intrusion Prevention Systems (NGFW), and fraud prevention tools. F5's anti-fraud solution is called F5 WebSafe and is designed to combat account theft, detect signs of malware infection, keylogging, phishing, Remote Access Trojans (RATs), and attacks like MITM (Man in the Middle), MITB (Man in the Browser) and MITP (Man in the Phone - hacking mobile devices). At the same time, F5 WebSafe uses various methods to identify fraudulent activities, for example, attempts to automatically translate, especially the introduction of malicious programs such as Zeus, Citadel, Carberp. At the same time, the system analyzes the digital profiles of devices and users.
Figure 17. Diagram of F5 WebSafe System Operation
F5 WebSafe Features:
IBM Trusteer Rapport
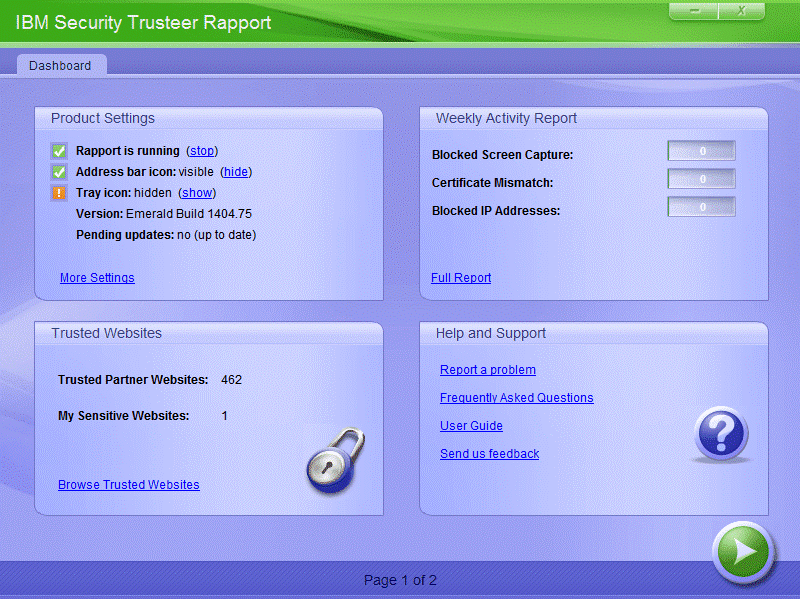
The IBM Trusteer Rapport from IBM is designed to protect users from credential hijacking, screen capture, malware, and phishing attacks, including attacks such as MITM and MITB. To do this, IBM Trusteer Rapport uses machine learning technologies to automatically detect and remove malware from the endpoint device, ensuring a secure online session.
Figure 18. IBM Trusteer Rapport system interface
Features of IBM Trusteer Rapport:
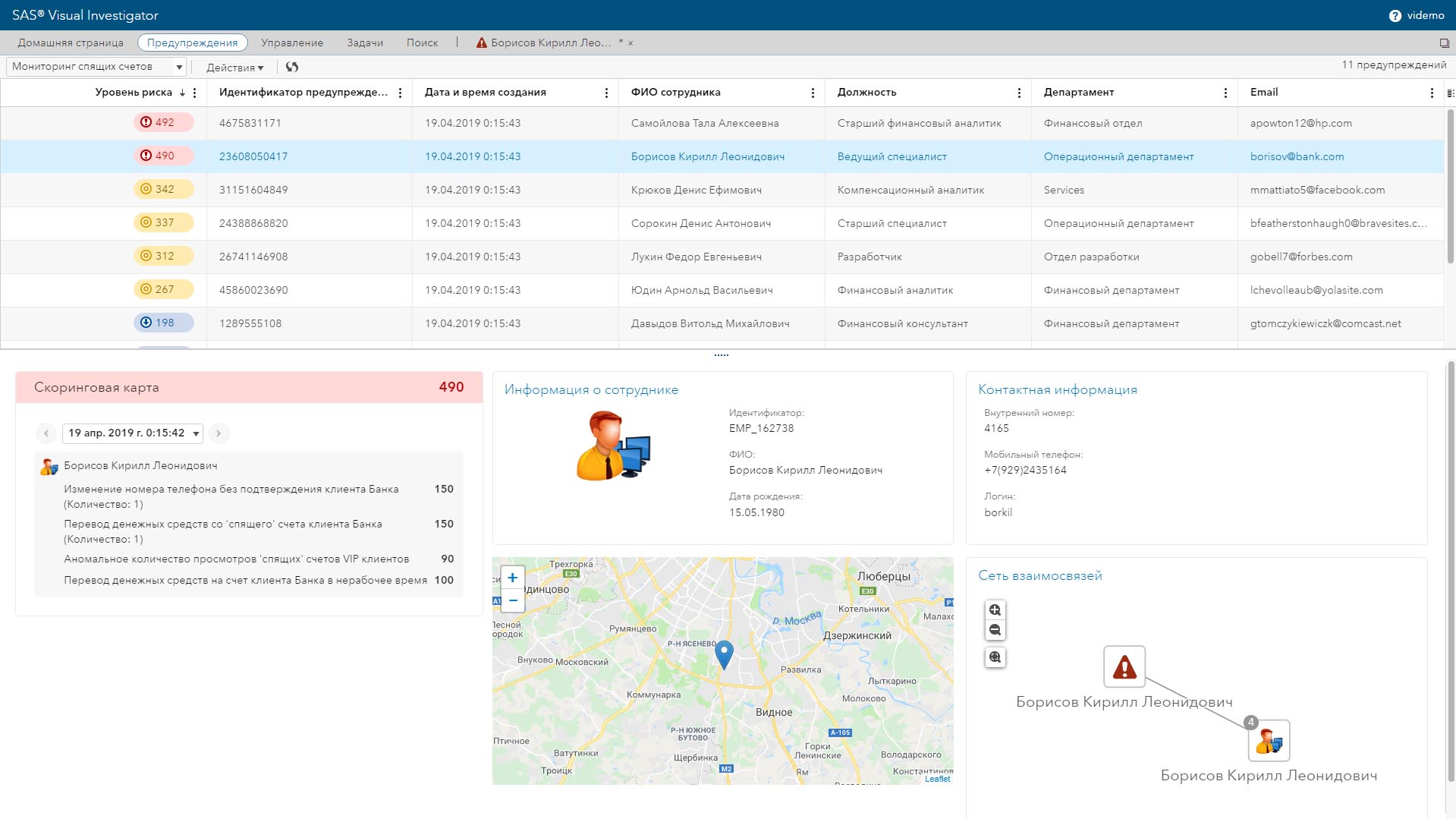
Kaspersky Fraud Prevention
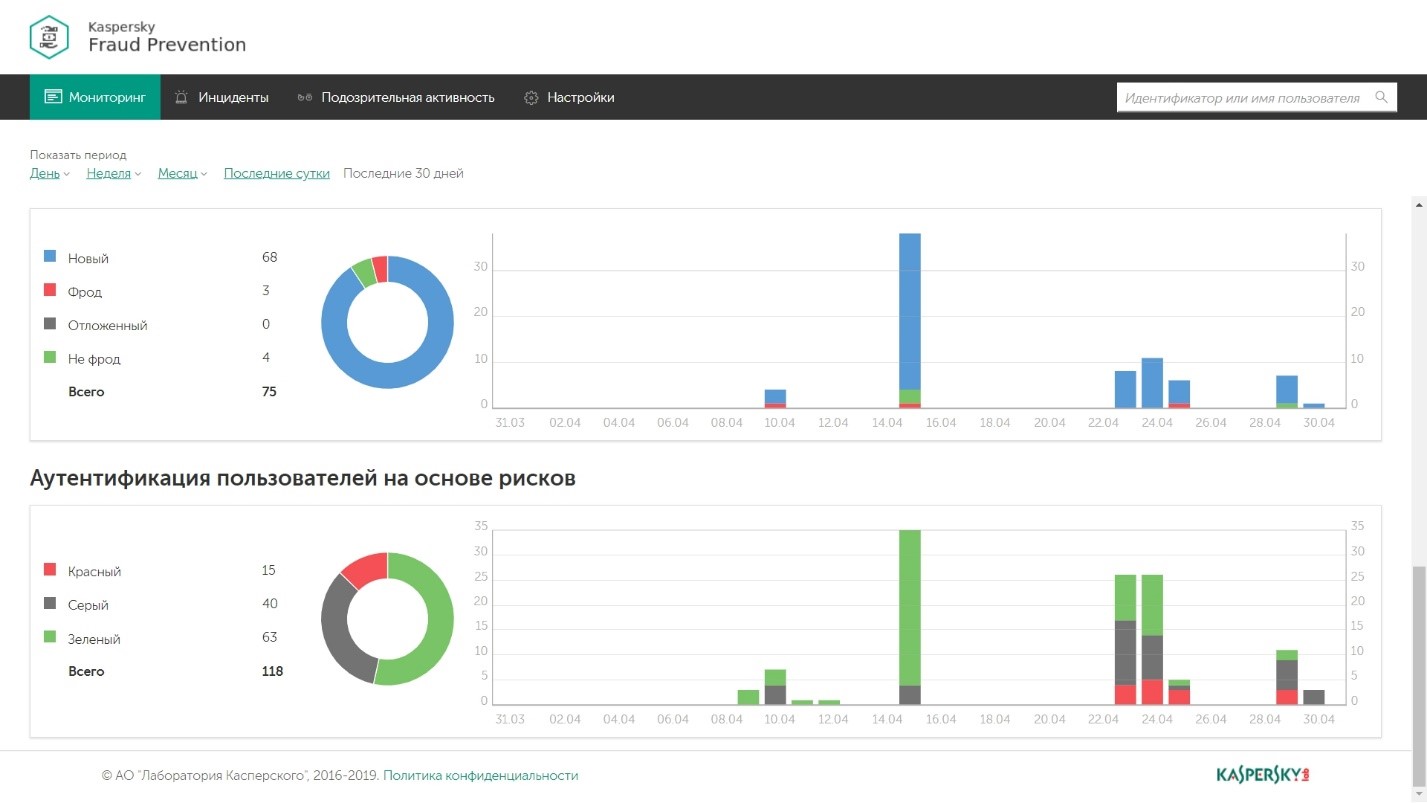
Kaspersky Lab was founded in 1997 (Moscow). The company initially specialized in the development of protection tools for endpoint workstations, including anti-virus solutions for both private and commercial use. Currently, Kaspersky Lab is developing products aimed at securing virtual and cloud environments, critical infrastructures and protection against cyber fraud. The Kaspersky Fraud Prevention solution from Kaspersky Lab is designed to solve the problem of digital fraud in online banking, retail, government services, online games and other industries that use websites and mobile applications to provide their services. As part of the Kaspersky Fraud Prevention solution, two products have been implemented: Automated Fraud Analytics, which detects account thefts in real time, detects malicious programs in web applications and mobile devices without installing additional applications, in-depth study of fraudulent account creation and money laundering. Advanced Authentication, which provides risk-based authentication results. This improves the security of the authentication process, improves the user experience, and reduces the cost of classic user authentication approaches.
Figure 19. Interface of the Kaspersky Fraud Prevention system
Features of Kaspersky Fraud Prevention:
ThreatMetrix
The RELX Group company was founded in 1993 (London, Great Britain). RELX Group is an international information and analytical company specializing in 4 main segments: science, technology and medicine, business analytics and risk management, legislation. In 2018, the company acquired ThreatMetrix. ThreatMetrix from RELX Group evaluates the context of each transaction in real time, analyzing device data, location and other identification data to detect abnormal behavior. ThreatMetrix helps protect against fraudulent attacks, including attacks based on location spoofing, MITM, MITB, hidden malware, unusual botnet behavior.
Figure 20. Main features of the ThreatMetrix system

ThreatMetrix features:
Group-IB Secure Bank
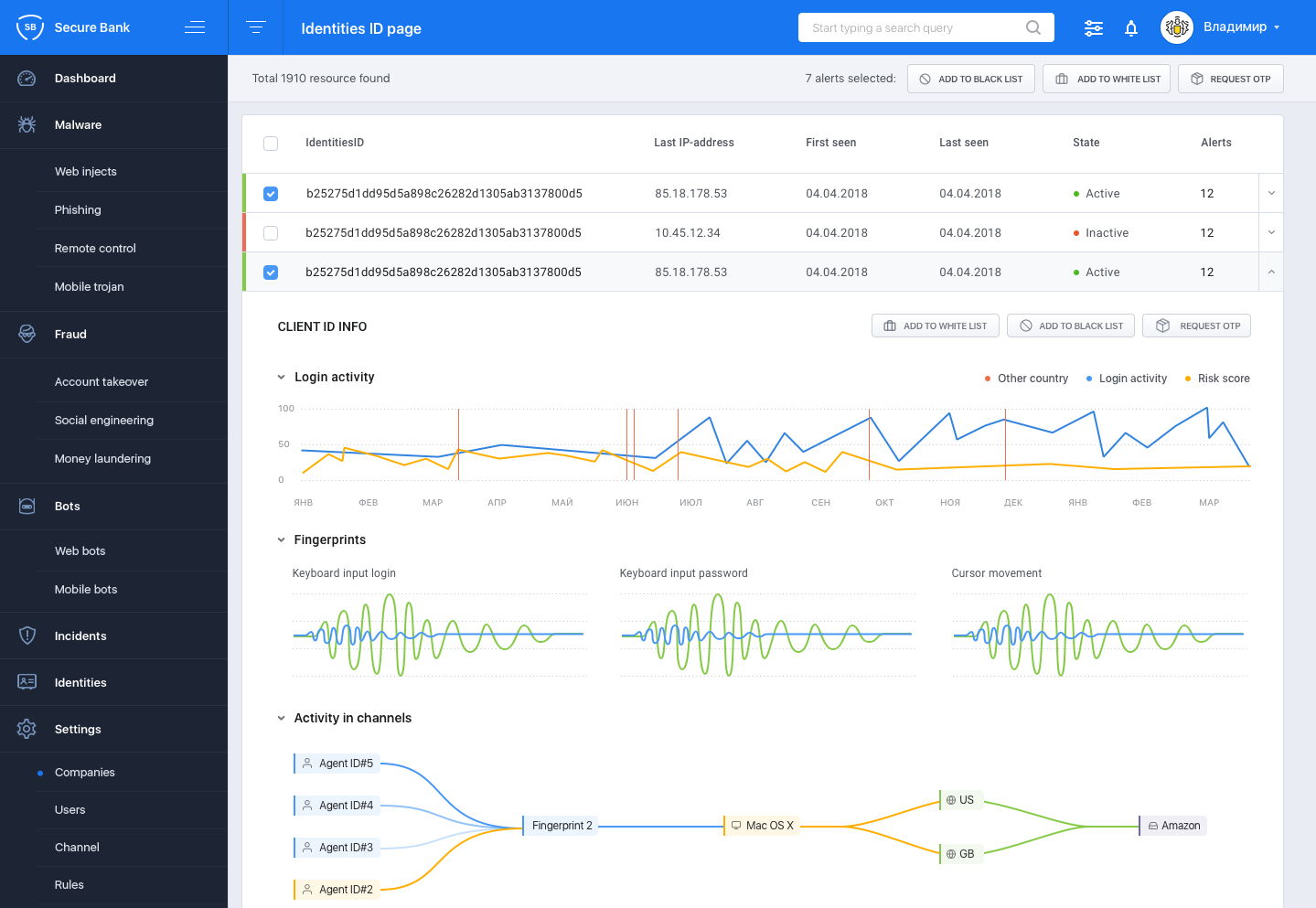
Group-IB was founded in 2003 (Moscow). The main areas of the company are the prevention and investigation of cybercrimes, incident response, computer forensics, consulting and audit of information security systems. Group-IB develops early warning systems for cyber threats, including products to protect against hacker attacks, theft and fraud. Group-IB's anti-fraud system is called Secure Bank and performs such functions as detecting and preventing fraud in real time on the bank's client side, including detecting social engineering, protecting against payment fraud (including from using P2P pages for theft, CNP fraud and automatic substitution of payment details), protection against banking Trojans, detection of cross-channel fraud (attacks through online portals and mobile devices), as well as protection against credit fraud (bot activity on the application page, work of credit brokers, counterfeit loan application). In addition, the system identifies customers' devices and provides their power of attorney scores to the bank, thus optimizing the bank's fraud costs and improving the user experience.
Figure 21. Interface of the Secure Bank system
Features of Secure Bank:
WEB ANTIFRAUD
The WEB ANTIFRAUD company was founded in 2017 (Moscow). The company specializes in the development of systems for monitoring and combating fraud with user accounts in banking and other online financial services. The WEB ANTIFRAUD system is aimed at preventing the theft of user accounts in online services. For this, the formation of a fingerprint and analysis of the user's device, analysis of behavior on the site, search for the presence of Trojans in browsers (including automatic transfer of funds and MITB attacks), search for accounts belonging to the same owner (in order to implement measures to prevent money laundering, AML), as well as other technical tools to prevent fraudulent activities on the online service website. Antifraud solution WEB ANTIFRAUD works automatically without human intervention, but, if necessary, provides detailed analytics on incidents that have occurred. WEB ANTIFRAUD helps you decide on the need for two-factor authentication on a case-by-case basis, and also reports security incidents and signs of account theft.
Figure 22. WEB ANTIFRAUD system interface
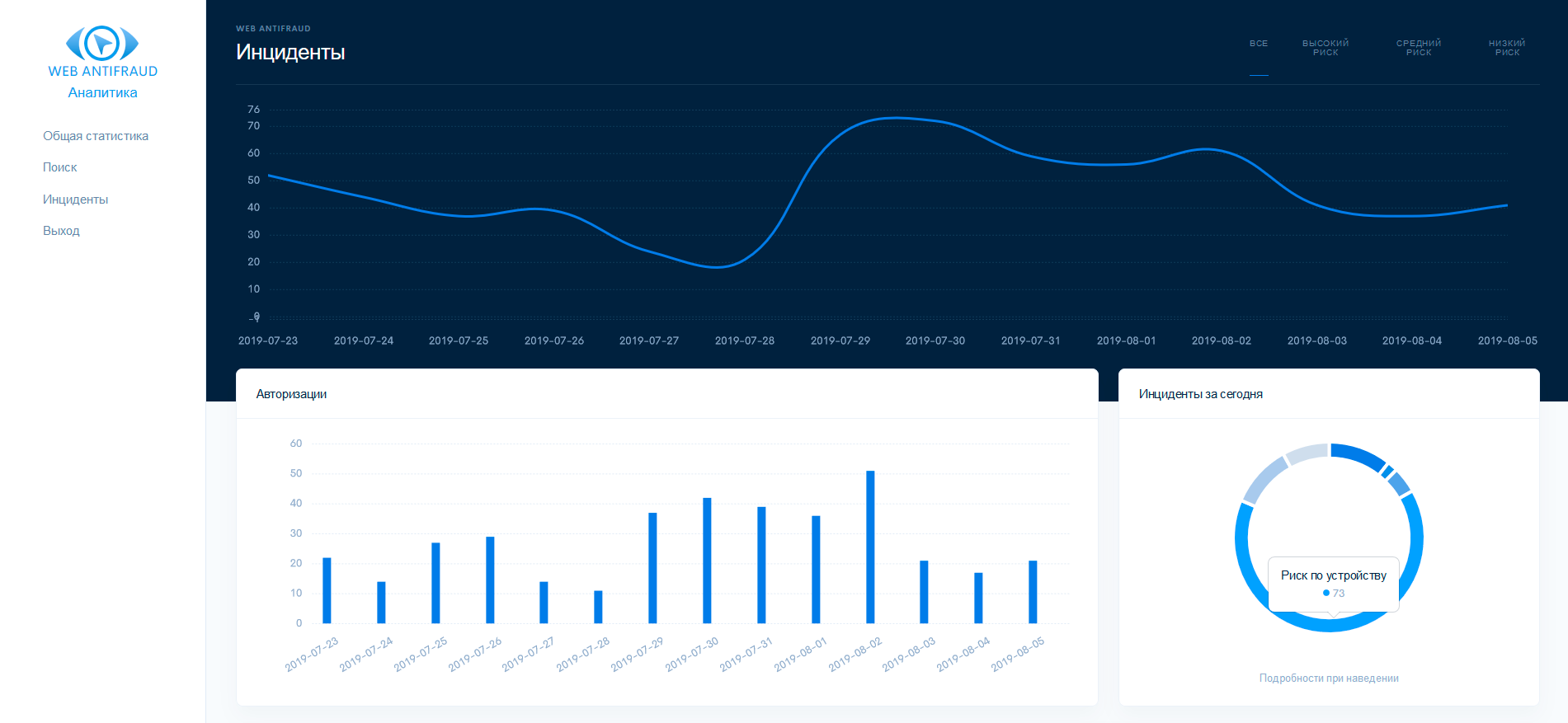
Features of WEB ANTIFRAUD:
Highly specialized systems for detecting signs of banking fraud
FPS.Bio
The VisionLabs company was founded in 2012 (Moscow). The company develops software in the field of computer vision and machine learning. In particular, VisionLabs specializes in the creation of products and solutions in the field of face and object recognition, as well as augmented and virtual reality. The system of combating banking fraud FPS.Bio from the VisionLabs company belongs to the class of highly specialized platforms. The system is developed on the basis of a solution for biometric verification and identification of individuals. The core of FPS.Bio is a neural network, which, according to the developers, uses unique algorithms. The functions of the system include the formation of a biometric portrait of a client, comparing it with millions of similar portraits and providing results for decision-making.
Figure 23. Organization of work when using FPS.Bio
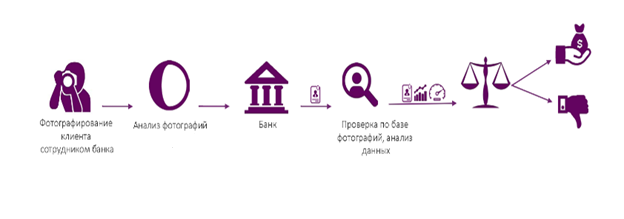
Features of FPS.Bio:
SmartTracker.FRAUD
The Speech Technology Center company was founded in 1990 (St. Petersburg). The company specializes in the development of systems in the field of biometrics, high-quality recording, processing and analysis of audio and video information, speech synthesis and recognition. The software and hardware complex for photobiometric identification SmartTracker.FRAUD allows you to replace the verification of the authenticity of documents and information provided by the clients of the bank with a completely different method based on the control of identification of appearance (the information that a person cannot forge).
Figure 24. How SmartTracker.FRAUD works
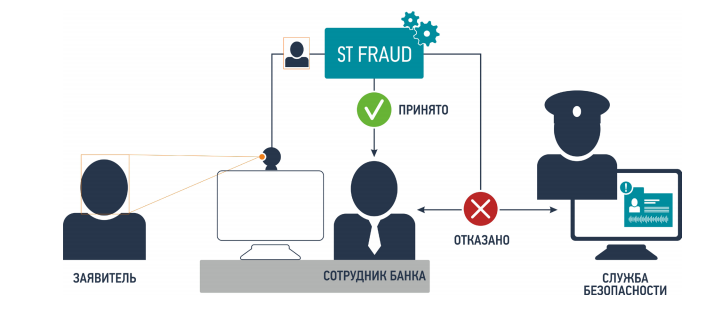
Features of SmartTracker.FRAUD:
Mixed anti-bank fraud systems
RSA Adaptive Authentication and Transaction Monitoring RSA was founded in 1982 (Bedford, Massachusetts, USA). The company specializes in computer and network security, including software development for network security, two-factor authentication, fraud prevention, identification and access control. RSA Transaction Monitoring and Adaptive Authentication from RSA belongs to the class 1 general analytics platforms, but includes capabilities and 2 classes. The system detects fraudulent attempts in real time and monitors transactions after a user logs in to protect against attacks such as MITM and MITB. At the same time, RSA Transaction Monitoring and Adaptive Authentication can be implemented both on the servers of the organization and used as a cloud service.
Figure 25. Diagram of the RSA Adaptive Authentication and Transaction Monitoring system
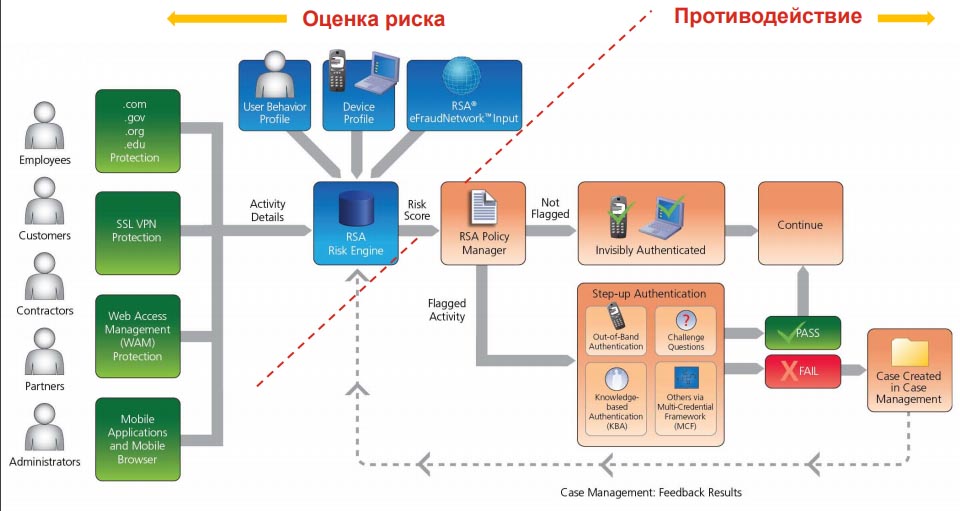
Features of RSA Transaction Monitoring and Adaptive Authentication:
BI.ZONE Cloud Fraud Prevention
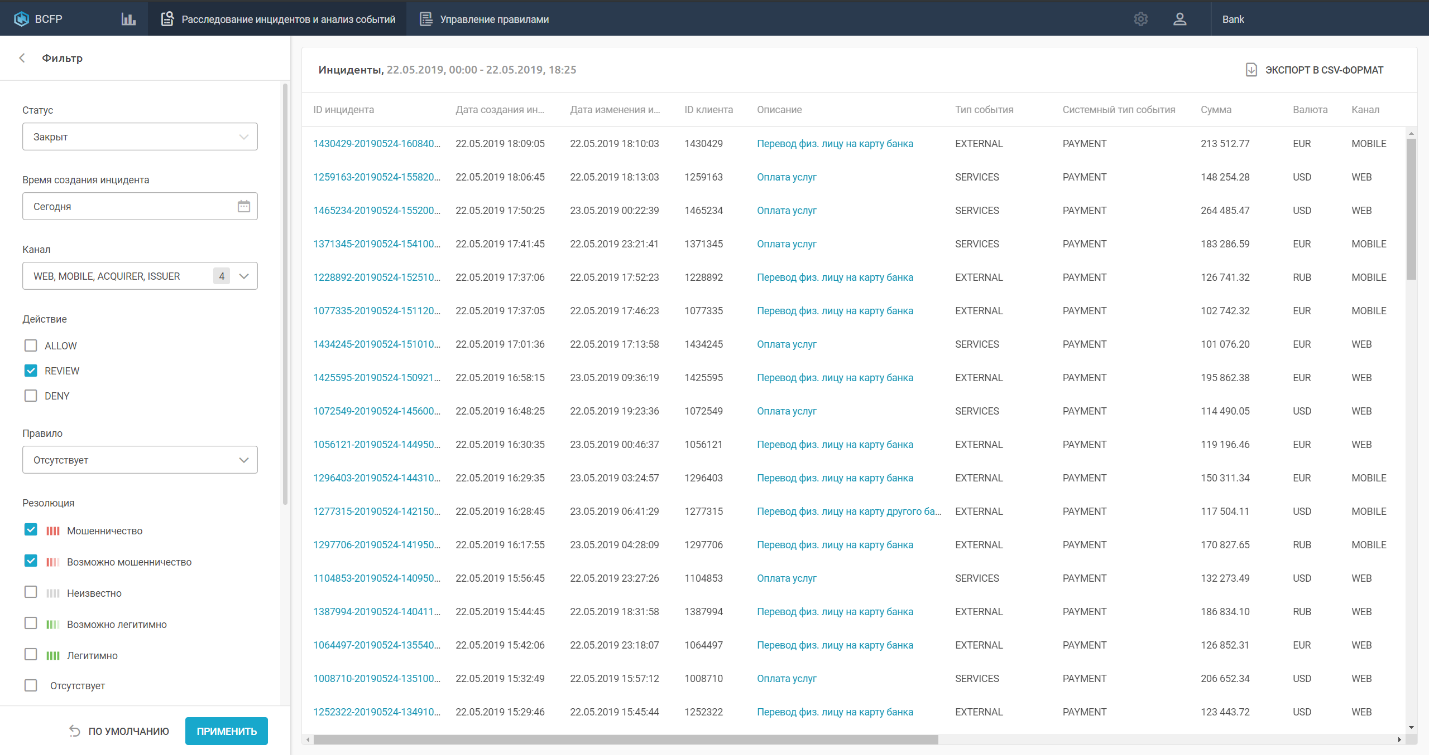
BI.ZONE was founded in 2016 and today provides more than 30 cybersecurity services: from cyber intelligence, consulting to cybercrime investigation, and also develops its own technology products and automated solutions to protect IT infrastructures and applications. BI.ZONE products maximally automate the processes of detecting and preventing cyber attacks, and the applied machine learning and artificial intelligence technologies allow detecting attacks and fraud at an early stage. BI.ZONE Cloud Fraud Prevention antifraud system includes both class 1 and class 2 platform capabilities. It is designed for cross-channel monitoring and analysis of payments in such channels as Internet banking, bank-client, mobile bank, issue, acquiring. BI.ZONE Cloud Fraud Prevention checks all payments made in real time and, using machine learning and a system of rules, prevents fraudulent transactions. The solution automatically builds a client profile, taking into account session and payment transactions, a digital "fingerprint" of the device, which allows checking transactions for compliance with the client's behavior model and detecting anomalies.
Figure 26. BI.ZONE Cloud Fraud Prevention system interface
Key Features
The first attack by hackers from the DPRK Lazarus on Russia was recorded findings Banking fraud continues to progress every year. Therefore, the market for anti-banking fraud systems is growing. The USA is the leader in this area. However, ensuring security against fraud is also relevant for Russian financial institutions.
When choosing an anti-fraud system, you must first decide what tasks it should perform. In most cases, in order to protect a bank from fraud, it will be necessary to use several classes of anti-fraud systems. At the same time, when choosing general analytical platforms, one should pay attention to the complexity of implementation and ease of use, and when choosing systems that we classified as class 2, it is worth paying attention to the methods used (for example, schemes for detecting malicious programs, remote control capabilities, etc.). Class 3 products can complement the security system, since each product solves a highly specialized task (recognizes images, speech, etc.)
anti-malware.ru
1. Introduction
1. The global market for anti-bank fraud systems
3. The market for anti-banking fraud systems in Russia
4. Functions of anti-bank fraud systems
5. A Brief Overview of Anti-Bank Fraud Systems
5.1. Comprehensive banking fraud and anomaly detection systems
5.1.1. ARIC White Label
5.1.2. FICO Application Fraud Manager
5.1.3. FraudWall
5.1.4. FRAUD-Analysis
5.1.5. IBM Safer Payments
5.1.6. Intellinx
5.1.7. Jet detective
5.1.8. Nice actimize
5.1.9. SAS Fraud and Security Intelligence
5.1.10. Smart Fraud Detection
5.2. Systems for identifying banking fraud instruments
5.2.1. Threat detector
5.2.2. Digital Banking Fraud Detection
5.2.3. F5 WebSafe
5.2.4. IBM Trusteer Rapport
5.2.5. Kaspersky Fraud Prevention
5.2.6. ThreatMetrix
5.2.7. Group-IB Secure Bank
5.2.8. WEB ANTIFRAUD
5.3. Highly specialized systems for detecting signs of banking fraud
5.3.1. FPS.Bio
5.3.2. SmartTracker.FRAUD
5.4. Mixed anti-bank fraud systems
5.4.1. RSA Adaptive Authentication and Transaction Monitoring
5.4.2. BI.ZONE Cloud Fraud Prevention
6. Findings
Introduction
Since many banking and payment transactions have moved into the field of informatization, fraud in this area has been actively developing. The most famous attacks on banking systems in the past few years have been carried out by the criminal gangs Cobalt, Carbanak, Lazarus and Lurk. According to Sberbank's estimates, Russia's losses from cyberattacks amount to about 650 billion rubles a year. At the same time, in the first two weeks of 2019 alone, Sberbank was subjected to 18 cyber attacks. Cybercriminals carry out attacks on interbank transfer systems, card processing, ATM management, Internet banking and payment gateways.
According to the Positive Technologies report, attackers use a simple attack scenario that consists of 5 sequential stages:
1. Preliminary exploration and preparatory work.
2. Penetration into the internal network.
3. Anchoring in the internal network and developing the attack.
4. Compromise of banking systems and theft of funds.
5. Hiding traces.
These stages are relevant when phishing, infecting a victim's computer or smartphone with previously known malware, conducting man-in-the-middle attacks, using keyloggers and even zero-day vulnerabilities.
Group-IB specialists identified 7 common schemes of theft of funds during attacks on remote banking systems (RBS):
- social engineering;
- transfers from card to card;
- transfers via online banking;
- interception of access to mobile banking;
- fake mobile banking;
- purchases with Apple Pay and Google Pay;
- theft through SMS banking.
The global market for anti-bank fraud systems
In 2020, the global market for anti-fraud systems was valued at US $ 13.59 billion. The scale is projected to reach $ 31.15 billion (CAGR = 16.42%) for 2024. This is due to the increased opportunities for fraud due to the increase in the number of transactions (both monetary and information-oriented), technological advances, as well as the general digitalization of the financial sector.
Figure 1. Market size of antifraud systems in the world by region (North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, Central Asia and Africa, Latin America)

According to Markets and Markets reports, the following companies are the main providers of anti-banking fraud systems around the world:
- IBM (USA);
- FICO (USA);
- SAS Institute (USA);
- BAE Systems (UK);
- NICE Systems (Israel);
- LexisNexis Risk solutions (USA), etc.
Figure 2. Rating of anti-fraud systems developers, according to The Forrester Wave

The market for anti-banking fraud systems in Russia
The antifraud systems market in Russia has gone through several characteristic stages of development. Evolutionary breakthroughs were such important milestones as the emergence of Chip Liability Shift in 2007-2008, and before that the emergence of a standard for monitoring bank card transactions from Visa in 2003, which gave impetus to the components of antifraud systems in processing. In 2011-2012. there was a massive series of attacks on remote banking systems, initially affecting mainly legal entities and subsequently spreading to citizens. In 2014-2015. banking Trojan Lurk and other malicious programs gave impetus to the emergence of Russian solutions from Group-IB and Kaspersky Lab. In 2018, the adopted Federal Law of June 27, 2018 No. 167-FZ "On Amendments to Certain Legislative Acts of the Russian Federation Regarding Countering the Theft of Funds" again heated the issue of anti-fraud systems, especially for those representatives of the credit and financial sector, for whom the acts of implementation of transactional fraud were small and in fact measured below the cost of the anti-fraud solutions themselves. According to Sberbank, in 2018, with the help of the introduced anti-fraud system, it was possible to save more than 32 billion rubles belonging to depositors.
Functions of anti-bank fraud systems
The fraud detection and prevention process does not have an initial or final stage, it must be carried out continuously and include the following sub-processes:
Monitoring;
Detection;
Making decisions;
Training.
Figure 3. The principle of operation of anti-fraud systems

Anti-fraud systems can have the following technologies and capabilities in their arsenal:
- Text analytics that is performed using search technologies, content categorization, and entity extraction.
- The calculation of statistical parameters, which is used to identify deviations that could indicate fraud.
- Network analytics, which is used to identify connections, identify patterns.
- Gap testing is about finding any missing elements in the serial data where they shouldn't be.
- Login Date Confirmation is used to assess inappropriate or suspicious times for posting or entering information.
- Supervised machine learning based on historical data to identify specific patterns.
- Unsupervised learning, which involves analyzing and evaluating data that does not contain information about the identified fraud. Used to detect new anomalies.
All anti-fraud systems have the same function - to detect and prevent fraud. However, they can solve this problem in different ways and compare anti-fraud systems without additional classification is a wrong decision.
So, for example, there are so-called core-systems - powerful analytical platforms that allow you to implement logic in separate segments (RBS or bank card processing), there are also specialized systems that control the parameters of devices and risks on their side. And at the same time, separate systems are being developed, sharpened for the recognition of photo, video, speech. Many of the systems do not compete, but, on the contrary, complement each other's functions. For example, a specific highly specialized solution cannot by itself cover the requirements of the Federal Law of 27.06.
Based on this, we have divided the existing systems for combating banking fraud into 3 classes:
1 class. Solutions of this class are aimed at detecting and identifying traces of fraud and detecting anomalies.
2 class. Solutions of this class are aimed at identifying fraud tools, cause or risk (for example, the presence of malware, remote control components, phishing components).
3 class. Solutions of this class solve highly specialized tasks. In particular, they can be designed for image recognition to detect fraud, and can be equipped with a speech recognition system.
A Brief Overview of Anti-Bank Fraud Systems
Comprehensive banking fraud and anomaly detection systems.
ARIC White Label
Featurespace was founded in 2008 (Cambridge, UK). The company was founded by a professor at the University of Cambridge with the goal of developing an adaptive behavioral analytics engine that enables fraud protection based on anomaly detection. Featurespace's ARIC White Label system belongs to the class of general analytical platforms. The system uses machine learning technologies to provide protection against fraudulent transactions for various types of payments (cards, e-wallets, etc.) in real time. In ARIC White Label, models of normal customer behavior are created, deviations in which are subsequently recorded by the system. Different analysis rules can be created for different clients, they can also be given access to the ARIC White Label to set up their own rules and models for work.
Figure 4. ARIC White Label system interface

Features of ARIC White Label:
- Customizing the system interface and providing access to the system.
- Preventing not only common fraudulent activities, but also money laundering (AML) activities.
- Leverage machine learning and behavioral analysis technologies to help protect against malware, bot attacks, and chargeback fraud.
- The ability to use ARIC White Label as a cloud service.
FICO Application Fraud Manager
FICO was founded in 1956 (San Jose, California, USA). The company specializes in the development of predictive analytics and decision making software, including solutions for assessing credit risks, as well as reducing losses from fraudulent activities.
The FICO Application Fraud Manager system from FICO belongs to a general analytical platform and real-time identification of fraud attempts through an analytical system that uses machine learning and adaptive analysis technologies. The solution can be installed both locally and used using SaaS technology. The system allows you to prevent fraudulent attempts by third parties, as well as attempts to deliberately abuse account privileges aimed at fraud with credit and debit payment cards, electronic payments, and deposit accounts.
Figure 5. Diagram of the FICO Application Fraud Manager system

Features of FICO Application Fraud Manager:
- Using machine learning technologies.
- The ability to use the platform as a cloud service.
- Advanced link and social media analysis for client monitoring.
- Investigation of incidents with the ability to assign roles and provide reporting.
FraudWall
The Frodeks company was founded in 2011 (Ufa). The company specializes in information security services, development and implementation of intelligent systems for detecting fraudulent payments, data processing systems, and information security investigations. Frodex's flagship solution is FraudWall, a fraudulent payment detection system, which has been assigned a class of information systems for solving specific industry problems. The FraudWall system from the Frodex company can be classified as a general analytical platform. It is designed to prevent theft of client funds in remote banking systems (RBS), to combat internal fraud (for example, unauthorized payments in the ABS), to prevent the theft of bank funds through the AWS KBR. When the system detects a suspicious payment, it makes a call to the client and conducts live communication with him, recognizing the client's responses. Upon completion of the call, FraudWall decides to execute the payment or stop the operation.
Figure 6. FraudWall system interface

FraudWall features:
- Scalability of the solution.
- Integration with a specialized speech recognition system VoiceNavigator from the Center for Speech Technologies.
- Integration with FraudMonitor interbank system and blacklists.
- Several options for implementation into the bank's network (direct connection to the RB or ABS database, connection as a web server of the RB system, connection in the role of an intermediate proxy server between the bank client and the RB system web server).
FRAUD-Analysis
Bank Software Systems (BSS) was founded in 1994 (Moscow). The main direction of the company is the development and implementation of automated systems for remote banking and financial management. In addition to complex systems for the financial market, BSS develops specialized products, including FRAUD-Analysis. The FRAUD-Analysis system from BSS can be classified as a general analytical platform, but the system is designed primarily to prevent fraud when servicing individuals and legal entities by the bank within the framework of BSS's own solutions. FRAUD analysis is capable of protecting against threats of using stolen authentication means and the private key of an electronic signature, threats of access to an open session of working with the system, threats of altering payment document details (for example, using malware).
Figure 8. Diagram of the FRAUD-Analysis system

Features of FRAUD-Analysis:
- Informing the security administrator by sending SMS messages or e-mails.
- Suspension of sending a suspicious document until a decision is made by the security administrator.
- Flexible configuration of rules for the security administrator and provision of the check result to the RBS system in automatic mode.
IBM Safer Payments
IBM was founded in 1911 (Armonk, New York, USA). The company is one of the world's largest manufacturers and suppliers of hardware and software, IT services and consulting services. The company has a subsidiary Trusteer, which deals with computer security, including the development of anti-fraud systems. The IBM Safer Payments solution from IBM is a common analytics platform. It is developed on the IRIS platform following the IBM acquisition of IRIS Analytics. The system is designed to detect fraud attempts in real time. At the same time, security is ensured both when making non-cash payments in many systems (automated clearing houses, acquiring banks, the Single Euro Payments Area, Chip & Pin and others), and through merchant terminals, ATMs, online and mobile banks.
Figure 8. IBM Safer Payments system interface

Features of IBM Safer Payments:
- Using machine learning and cognitive computing technologies to prevent fraud.
- Using parallel computing technologies to speed up query processing.
- Ability to profile various entities and detect abnormal behavior.
Intellinx
Intellinx Ltd. founded in 2005 (Or Yehuda, Israel). The company develops solutions for tracking end-user activities and preventing data leaks from organizations. At the same time, the means of protection are aimed at protecting both from outside violators and from employees of organizations. Intellinx solution from Intellinx Ltd. belongs to the class of general analytical platforms. The system enables compliance with regulatory requirements such as Basel II, STO BR IBBS and others by detecting identity theft attempts and other types of fraud in Internet banking and other online services. At the same time, Intellinx can track the activity of system administrators and other privileged users, monitor availability and response time in critical processes. The system can track cases of compromised PIN codes, as well as attempts to carry out transactions on the same account from different locations in a short period of time.
Figure 9. Diagram of the Intellinx system

Intellinx features:
- The ability to receive data directly from network traffic.
- Possibility of installation in a gap or in detection mode only.
- Unlimited complexity of control options.
- Controlling the actions of privileged users.
- Compliance control.
Jet detective
Jet Infosystems was founded in 1991 (Moscow). One of the directions of the company is information security and development of solutions to ensure the security of commercial and government organizations. Jet Infosystems specializes in the construction of integrated security systems, protection of cloud infrastructure, incident management, as well as anti-fraud and income guarantee systems in the banking and telecommunications sectors, retail, as well as in the fuel and energy complex. Jet Detective antifraud system from Jet Infosystems is a general analytical cross-channel platform and performs such functions as countering internal and third-party fraud, monitoring business processes, behavioral analytics for employees, customers and business systems, as well as checking for compliance with requirements. The application is developed in accordance with a three-tier architecture - client, application server and data storage layer - and consists of 6 functional modules (Desktop, Data Factory, Event Analysis, Incident Investigation, Machine Learning, Authorization). The product fully complies with the current requirements of the legislation of the Russian Federation on combating fraud and ensuring AML / CFT.
Figure 10. Jet Detective System Interface

Features of Jet Detective:
- Real-time event processing.
- Using the Big Data platform instead of the usual relational database management systems.
- Use of self-learning mathematical models that automatically detect suspicious actions.
- Conducting investigations of information security incidents related to identified anomalies.
- Predicting potential anomalies.
Nice actimize
NICE Systems Ltd. founded in 1986 (Ra'anana, Israel). The company develops both cloud-based and on-premise software to improve customer experience for businesses, comply with regulations, and prevent financial crime. Nice Actimize solution from NICE Systems Ltd. belongs to the class of general analytic platforms and allows detecting, preventing and investigating cases of money laundering through built-in AML lifecycle management and fraud in real time. The system provides protection for all types of payments, including SWIFT / Wire, Faster Payments, BACS SEPA payments, ATM / debit transactions, bulk payments, invoice payments, P2P / postal payments and various forms of internal transfers available in various markets.
Figure 11. Nice Actimize system interface

Nice Actimize Features:
- Support for multiple methods and capabilities for user authentication.
- Multichannel monitoring.
- Protection of transactions on mobile devices, IVR and contact centers.
- The ability to use as a cloud service.
- Using machine learning technologies to create universal templates.
SAS Fraud and Security Intelligence
SAS was founded in 1976 (Cary, North Carolina, USA). The company is a large private IT company in the world and specializes in the development of technological software and applications of the Business Intelligence, Data Quality and Business Analytics classes. SAS has developed a comprehensive SAS Fraud and Security Intelligence (SAS FSI) solution that provides a unified platform for addressing the challenges of preventing transactional, credit, internal and other types of fraud. The SAS FSI solution belongs to the class of high-performance cross-channel platforms and is capable of processing thousands of transactions per second. It combines fine-tuning of business rules with machine learning technologies to prevent fraud with minimal positives. The investigation interface allows you to reveal hidden relationships between payment participants, and is also fully customizable to the needs of users. The block for working with machine learning models in the SAS system allows an ordinary user, without programming skills, to create a model and apply it to the transaction flow.
Figure 12. SAS FSI Component Interface

Features of SAS Fraud Management:
- Decision making in milliseconds.
- Easy integration with business systems, authentication services and data warehouses.
- Using the technology of self-learning neural networks on the stream for effective fraud detection with a minimum level of triggers.
- Functional rule constructor.
- Tools for fine-tuning the investigation interface to the needs of users, with the ability to search the map, identify hidden relationships and create business processes for investigating incidents.
Smart Fraud Detection
Fuzzy Logic Labs has been developing, implementing and supporting software in the field of banking antifraud since 2011. Smart Fraud Detection system is designed to counter fraudulent transactions in various customer service channels: RBS for retail and corporate business; mobile and SMS bank; processing of plastic cards (emission); payment terminals, acquiring, internet acquiring; operations and calls through IVR and call center employees; actions and operations of bank employees in the office; operations using instant messengers and chat bots.
Figure 13. Scheme of the Smart Fraud Detection system

The Smart Fraud Detection system can solve tasks for three classes of fraud monitoring in banks. The system checks payments in real time, builds operator and client profiles, recognizes employee behavior using cameras and microphones, monitors transaction dependencies in different business areas and in different systems of the bank's IT architecture. The main activity of the company is combating external and internal fraud, as well as money laundering.
Figure 14. Incident card in the Smart Fraud Detection system interface

Features of the Smart Fraud Detection system:
- cross-channel and scalability;
- compatibility with processing systems Smart Vista, Compass +, WAY4;
- a combination of machine learning models and a rule method; own algorithmic developments: "Rule generator", "Personnel monitoring";
- highly specialized module of the 3rd class "for image and sound recognition";
- various integration protocols: HTTP / HTTPS (JSON), TCP (ISO 8583) and pre-configured functionality out of the box.
Systems for identifying banking fraud instruments
Threat detector
The BIFIT company (Banking and financial Internet technologies) was founded in 1999 (Moscow). The company specializes in the development of complex platforms for remote banking services, including for entrepreneurs, organizations, holdings and individuals. A feature of Internet banking systems from the BIFIT company is the use of Java technology, which makes it possible to expand the list of supported operating systems and client browsers. The "Threat Detector" module for protection against fraud of the BIFIT company is built into the iBank 2 system, which is designed to provide bank customers with services for remote account management. The general capabilities of the security subsystem include the use of an electronic signature mechanism, the use of cryptographic data transformation during transmission between the client and the bank, as well as the use of a cryptographic authentication mechanism of the parties. The built-in Threat Detector module allows you to detect malicious programs on a client's computer designed for theft in an RBS environment. At the same time, the security administrator has access to the ability to view information about infected workplaces of clients, the ability to analyze documents with which work was carried out on these workstations,
Figure 15. Threat Detector system interface

Features of iBank 2:
- No need to use imposed fraud prevention tools.
- Use of cryptographic libraries certified by the FSB of Russia.
- Detection of infected environments rather than fraudulent payments, which allows you to identify the threat ahead of time.
- Integration with solutions from Kaspersky Lab (Kaspersky Fraud Prevention) and IBM (IBM Trusteer).
Digital Banking Fraud Detection
Guardian Analytics was founded in 2005 (Mountain View, California, USA). The main focus of the company is the development of fraud prevention systems for financial institutions. The Digital Banking Fraud Detection system from Guardian Analytics belongs to the general analytical platforms. Like other fraud prevention systems, the system can be implemented both locally and as a cloud service. At the same time, Digital Banking Fraud Detection protects against attempts to hijack a client's account, fraudulent transfers, phishing and attacks like MITB in real time. A profile is created for each user, on the basis of which anomalous behavior is recognized.
Figure 16. Interface of Digital Banking Fraud Detection system

Features of Digital Banking Fraud Detection:
- The ability to work in the cloud.
- The use of machine learning technologies and behavioral analysis, which allows the system to adapt to new threats.
- The system is not based on compliance checking to reduce false positives.
- Using digital fingerprinting technology for devices.
F5 WebSafe F5 was founded in 1996 (Seattle, Washington, USA). The company develops information security systems, including Web Application Layer Firewalls (WAFs), DDoS protection systems, Next Generation Intrusion Prevention Systems (NGFW), and fraud prevention tools. F5's anti-fraud solution is called F5 WebSafe and is designed to combat account theft, detect signs of malware infection, keylogging, phishing, Remote Access Trojans (RATs), and attacks like MITM (Man in the Middle), MITB (Man in the Browser) and MITP (Man in the Phone - hacking mobile devices). At the same time, F5 WebSafe uses various methods to identify fraudulent activities, for example, attempts to automatically translate, especially the introduction of malicious programs such as Zeus, Citadel, Carberp. At the same time, the system analyzes the digital profiles of devices and users.
Figure 17. Diagram of F5 WebSafe System Operation

F5 WebSafe Features:
- Protection of end devices (including mobile devices, set-top boxes, game consoles) without installing additional applications.
- Advanced application-level encryption to protect against theft of credentials prior to transmission over SSL.
- The ability to integrate with systems of protection against DDoS attacks, WAF, SIEM, risk management systems and others.
- Analysis of digital profiles of devices and users.
IBM Trusteer Rapport
The IBM Trusteer Rapport from IBM is designed to protect users from credential hijacking, screen capture, malware, and phishing attacks, including attacks such as MITM and MITB. To do this, IBM Trusteer Rapport uses machine learning technologies to automatically detect and remove malware from the endpoint device, ensuring a secure online session.
Figure 18. IBM Trusteer Rapport system interface

Features of IBM Trusteer Rapport:
- Automatic detection and protection against phishing.
- Protect against malware by removing it on the target workstation.
- Protect against keylogging by encrypting keystrokes before sending them to the web browser.
- A global threat intelligence service that continually adds new threat intelligence to the system.
- The system is cloud-based, which reduces implementation costs.
Kaspersky Fraud Prevention
Kaspersky Lab was founded in 1997 (Moscow). The company initially specialized in the development of protection tools for endpoint workstations, including anti-virus solutions for both private and commercial use. Currently, Kaspersky Lab is developing products aimed at securing virtual and cloud environments, critical infrastructures and protection against cyber fraud. The Kaspersky Fraud Prevention solution from Kaspersky Lab is designed to solve the problem of digital fraud in online banking, retail, government services, online games and other industries that use websites and mobile applications to provide their services. As part of the Kaspersky Fraud Prevention solution, two products have been implemented: Automated Fraud Analytics, which detects account thefts in real time, detects malicious programs in web applications and mobile devices without installing additional applications, in-depth study of fraudulent account creation and money laundering. Advanced Authentication, which provides risk-based authentication results. This improves the security of the authentication process, improves the user experience, and reduces the cost of classic user authentication approaches.
Figure 19. Interface of the Kaspersky Fraud Prevention system

Features of Kaspersky Fraud Prevention:
- Continuous proactive detection of advanced fraud schemes prior to the transaction in real time.
- Cross-channel fraud detection (web and mobile).
- Use of behavioral biometrics (collection and analysis of data on keyboard use, mouse movement, use of mobile devices, etc.).
- The use of machine learning and behavioral analysis technologies to provide protection against malware and bot attacks.
- Analysis of digital profiles of users and devices.
- Preventing not only common fraudulent activities, but also money laundering (AML) activities through the ability to build and correlate relationships between users, sessions, devices and organizations.
ThreatMetrix
The RELX Group company was founded in 1993 (London, Great Britain). RELX Group is an international information and analytical company specializing in 4 main segments: science, technology and medicine, business analytics and risk management, legislation. In 2018, the company acquired ThreatMetrix. ThreatMetrix from RELX Group evaluates the context of each transaction in real time, analyzing device data, location and other identification data to detect abnormal behavior. ThreatMetrix helps protect against fraudulent attacks, including attacks based on location spoofing, MITM, MITB, hidden malware, unusual botnet behavior.
Figure 20. Main features of the ThreatMetrix system

ThreatMetrix features:
- Using machine learning technologies and behavioral analytics.
- Using the mobile SDK to protect against mobile fraud.
- The ability to use as a cloud service.
- Analytical reports with data on the activity of corporate applications.
Group-IB Secure Bank
Group-IB was founded in 2003 (Moscow). The main areas of the company are the prevention and investigation of cybercrimes, incident response, computer forensics, consulting and audit of information security systems. Group-IB develops early warning systems for cyber threats, including products to protect against hacker attacks, theft and fraud. Group-IB's anti-fraud system is called Secure Bank and performs such functions as detecting and preventing fraud in real time on the bank's client side, including detecting social engineering, protecting against payment fraud (including from using P2P pages for theft, CNP fraud and automatic substitution of payment details), protection against banking Trojans, detection of cross-channel fraud (attacks through online portals and mobile devices), as well as protection against credit fraud (bot activity on the application page, work of credit brokers, counterfeit loan application). In addition, the system identifies customers' devices and provides their power of attorney scores to the bank, thus optimizing the bank's fraud costs and improving the user experience.
Figure 21. Interface of the Secure Bank system

Features of Secure Bank:
- Use of Behavioral Analysis Technologies (UEBA) to combat social engineering, account hijacking, bots and other forms of fraud.
- Analysis of the technical characteristics of the device and browsers (digital fingerprint of devices).
- Creation of a global user profile that allows you to more accurately distinguish a legitimate client from a fraudster.
- An advanced rule engine that allows you to implement rules of any flexibility.
- JavaScript module embedded in the source code of web pages and mobile SDK for applications, protected from data spoofing and replay attacks.
- Ready integration with such anti-fraud systems as Fraud-Analysis, FraudWall, RSA, SAS, Intellinx, GBG Predator.
WEB ANTIFRAUD
The WEB ANTIFRAUD company was founded in 2017 (Moscow). The company specializes in the development of systems for monitoring and combating fraud with user accounts in banking and other online financial services. The WEB ANTIFRAUD system is aimed at preventing the theft of user accounts in online services. For this, the formation of a fingerprint and analysis of the user's device, analysis of behavior on the site, search for the presence of Trojans in browsers (including automatic transfer of funds and MITB attacks), search for accounts belonging to the same owner (in order to implement measures to prevent money laundering, AML), as well as other technical tools to prevent fraudulent activities on the online service website. Antifraud solution WEB ANTIFRAUD works automatically without human intervention, but, if necessary, provides detailed analytics on incidents that have occurred. WEB ANTIFRAUD helps you decide on the need for two-factor authentication on a case-by-case basis, and also reports security incidents and signs of account theft.
Figure 22. WEB ANTIFRAUD system interface

Features of WEB ANTIFRAUD:
- Determining the signs of fraud proactively at the stage of its preparation, and not after theft of funds.
- A set of rules and a behavior profile is created automatically for each individual user based on the results of his activity.
- All system decisions are made according to human-readable algorithms and do not contain the results of machine learning.
- Complements the internal transactional anti-fraud system, if available in the organization.
- Helps banks comply with the 167-FZ requirement to prevent money transfers without the client's consent.
- Extensive dashboard capabilities (incidents, search, account links, visualization, and more).
Highly specialized systems for detecting signs of banking fraud
FPS.Bio
The VisionLabs company was founded in 2012 (Moscow). The company develops software in the field of computer vision and machine learning. In particular, VisionLabs specializes in the creation of products and solutions in the field of face and object recognition, as well as augmented and virtual reality. The system of combating banking fraud FPS.Bio from the VisionLabs company belongs to the class of highly specialized platforms. The system is developed on the basis of a solution for biometric verification and identification of individuals. The core of FPS.Bio is a neural network, which, according to the developers, uses unique algorithms. The functions of the system include the formation of a biometric portrait of a client, comparing it with millions of similar portraits and providing results for decision-making.
Figure 23. Organization of work when using FPS.Bio

Features of FPS.Bio:
- Using neural network technologies. Formation of a biometric portrait of the client.
- Prevention of fraud in the issuance of loans by identifying the fact of forgery or the use of stolen documents.
SmartTracker.FRAUD
The Speech Technology Center company was founded in 1990 (St. Petersburg). The company specializes in the development of systems in the field of biometrics, high-quality recording, processing and analysis of audio and video information, speech synthesis and recognition. The software and hardware complex for photobiometric identification SmartTracker.FRAUD allows you to replace the verification of the authenticity of documents and information provided by the clients of the bank with a completely different method based on the control of identification of appearance (the information that a person cannot forge).
Figure 24. How SmartTracker.FRAUD works

Features of SmartTracker.FRAUD:
- Using biometric information to detect fraud.
- Preventing fraud when issuing loans in the office and when servicing remotely.
Mixed anti-bank fraud systems
RSA Adaptive Authentication and Transaction Monitoring RSA was founded in 1982 (Bedford, Massachusetts, USA). The company specializes in computer and network security, including software development for network security, two-factor authentication, fraud prevention, identification and access control. RSA Transaction Monitoring and Adaptive Authentication from RSA belongs to the class 1 general analytics platforms, but includes capabilities and 2 classes. The system detects fraudulent attempts in real time and monitors transactions after a user logs in to protect against attacks such as MITM and MITB. At the same time, RSA Transaction Monitoring and Adaptive Authentication can be implemented both on the servers of the organization and used as a cloud service.
Figure 25. Diagram of the RSA Adaptive Authentication and Transaction Monitoring system

Features of RSA Transaction Monitoring and Adaptive Authentication:
- The ability to work together with various authentication systems (login-password, SSO, EMV / CAP smart cards, using SMS messages, PKI systems, etc.).
- A handy tool for investigating information security incidents, including pre-installed reports.
- A scoring system for assessing risks, which is recalculated daily, keeping the analytical model of the system up to date.
- Self-learning technology.
BI.ZONE Cloud Fraud Prevention
BI.ZONE was founded in 2016 and today provides more than 30 cybersecurity services: from cyber intelligence, consulting to cybercrime investigation, and also develops its own technology products and automated solutions to protect IT infrastructures and applications. BI.ZONE products maximally automate the processes of detecting and preventing cyber attacks, and the applied machine learning and artificial intelligence technologies allow detecting attacks and fraud at an early stage. BI.ZONE Cloud Fraud Prevention antifraud system includes both class 1 and class 2 platform capabilities. It is designed for cross-channel monitoring and analysis of payments in such channels as Internet banking, bank-client, mobile bank, issue, acquiring. BI.ZONE Cloud Fraud Prevention checks all payments made in real time and, using machine learning and a system of rules, prevents fraudulent transactions. The solution automatically builds a client profile, taking into account session and payment transactions, a digital "fingerprint" of the device, which allows checking transactions for compliance with the client's behavior model and detecting anomalies.
Figure 26. BI.ZONE Cloud Fraud Prevention system interface

Key Features
- Cross-channel monitoring and analysis of transactions in various payment channels: internet bank, mobile bank, client bank, issue, acquiring.
- The ability to combine rule-based and model-based approaches to analyze transactions.
- Using Risk-Based Authentication (RBA) technology for Internet banking and mobile banking.
- Preventing not only fraudulent activities, but also solving the problems of compliance monitoring (AML).
- Convenient user interface for setting rules and investigating fraudulent transactions.
- Automatic risk assessment for each transaction, taking into account the configured rules, client profile, digital "fingerprint" of the device.
- JavaScript plug-in and mobile SDK for digital fingerprinting of devices.
- Machine learning using a set of models for automatic risk assessment, daily “self-learning” based on detected cases of fraud.
The first attack by hackers from the DPRK Lazarus on Russia was recorded findings Banking fraud continues to progress every year. Therefore, the market for anti-banking fraud systems is growing. The USA is the leader in this area. However, ensuring security against fraud is also relevant for Russian financial institutions.
When choosing an anti-fraud system, you must first decide what tasks it should perform. In most cases, in order to protect a bank from fraud, it will be necessary to use several classes of anti-fraud systems. At the same time, when choosing general analytical platforms, one should pay attention to the complexity of implementation and ease of use, and when choosing systems that we classified as class 2, it is worth paying attention to the methods used (for example, schemes for detecting malicious programs, remote control capabilities, etc.). Class 3 products can complement the security system, since each product solves a highly specialized task (recognizes images, speech, etc.)
anti-malware.ru
