Carding Forum
Professional
- Messages
- 2,788
- Reaction score
- 1,297
- Points
- 113
PaySpace Magazine has learned which financial companies are implementing solutions based on passive biometrics in Ukraine and around the world
Behavioral biometrics: the most effective solutions and in the world.
Several years ago, the American information platform TeleSign published a study according to which two-factor authentication and behavioral (or passive) biometrics will soon completely replace passwords. For example, in 2016, 9 out of 10 companies reported that behavioral biometrics would be a huge benefit to their security systems. 54% of companies expressed their intention to implement this method of protection in the future. The PaySpace Magazine editors found out which financial companies have taken up the implementation of this technology in Ukraine and the world.
Behavioral biometrics is a human recognition system that identifies a person by dynamic (behavioral) characteristics. Behavioral characteristics include handwriting and signature dynamics, voice and speech rhythm, gesture recognition, electronic device usage (typing speed, holding a smartphone or tablet), and even gait. Behavioral biometrics are also referred to as passive biometrics.
Today, the company offers customers a patented technology based on artificial intelligence, which in real time allows you to establish and confirm the identity of the client (in particular, by analyzing how the user holds the smartphone and how it controls it) to confirm the transaction or cancel it if signs of fraud are detected. The program also uses a built-in privacy algorithm to keep user data safe.
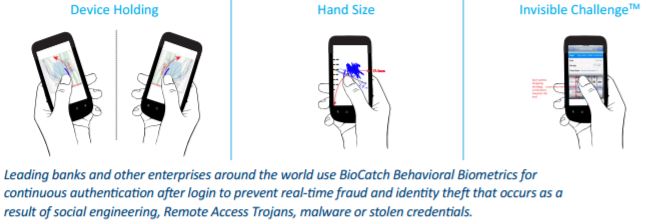
BioCatch analyzes the user's hand size and how he holds the device.
The BioCatch product is currently used by the Brazilian banking company Itaú Unibanco, the British large commercial bank NatWest and the American financial company American Express.
Usage example. One of BioCatch's largest clients, the Royal Bank of Scotland (RBS), is currently using the company's service to protect more than 18 million corporate and individual accounts. When logging into an RBS account, the program records more than 2 thousand interactive gestures of the client - from the angle at which he holds the mobile device to the fingers he uses to control the application. If the client uses the desktop version of the application, the program reads the speed of typing on the keyboard and pressing the mouse keys.
In 2018, the program recorded unusual activity coming from the account of one wealthy client. After authenticating, the visitor used the mouse scroll wheel - something the client had never done before. The user then entered the numbers at the top of the keyboard instead of the side they usually used. RBS blocked access to funds in the customer's account, which later turned out to be hacked.
According to Kevin Hanley, director of innovation at RBS, thanks to the development from BioCatch, the bank was able to prevent a fraudster from stealing a seven-figure amount from the client's account.
Criticism of passive biometrics. As noted by The New York Times, despite the successful prevention of fraud by the Royal Bank of Scotland, this case is perceived ambiguously. In particular, due to the fact that the user's behavior is not always constant, since the same person can behave differently in different situations due to fatigue, drunkenness, feeling unwell, or banal rush. The journalists also emphasized that a person can enter text in different ways, being behind a computer screen in the office and lying on the couch at home.
UnifyID: passive biometrics as a mobile app.In 2016, the American company UnifyID introduced a new system that analyzes user behavior and habits, his biometric characteristics, typing rhythm, location and movement, as well as how he interacts with different devices. Using machine learning, the program analyzes the information received, identifying the identity of the user. As the representatives of the company commented, the decision to resort to innovative solutions in the field of personal identification was made due to the unreliability of the systems available on the market.
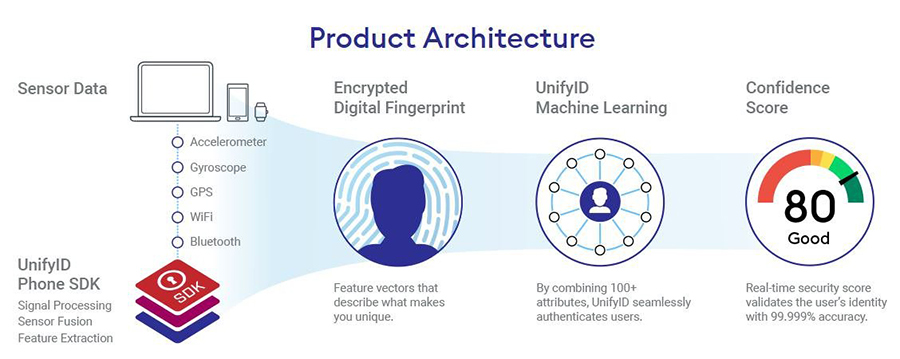
UnifyID analyzes biometric data of the user in real time.
The new system works as follows: the user needs to install a browser extension and a mobile application on his smartphone, which will study and eventually recognize it by the above characteristics.
The developers also took into account the fact that at first the user and the system will not be "familiar enough" for the program to instantly identify itself. To do this, at the initial stages of "dating", she will send a call to the user's phone, who will need to put his finger on the fingerprint scanner to confirm his identity.
Consumer data collected by the system is encrypted on the local device. Currently, the UnifyID product is available for iOS 10+ and Android 5.0+ users.
Banking application with passive biometrics. In 2016, the Nationwide Building Society, a British financial services provider, took over the development of a mobile banking application using behavioral biometrics . Tech companies BehavioSec and Unisys also took part in the project.
The Nationwide banking app, which is available for iOS and Android users, evaluates the user's actions, in particular, how he interacts with a smartphone or tablet. Passive biometrics are used to authenticate the consumer when making payments made in the app as an additional layer of protection.
In 2019, Nationwide announced that it would invest in Scaled Insights, a company that uses behavioral AI to analyze people's speech to communicate with users in their preferred language.
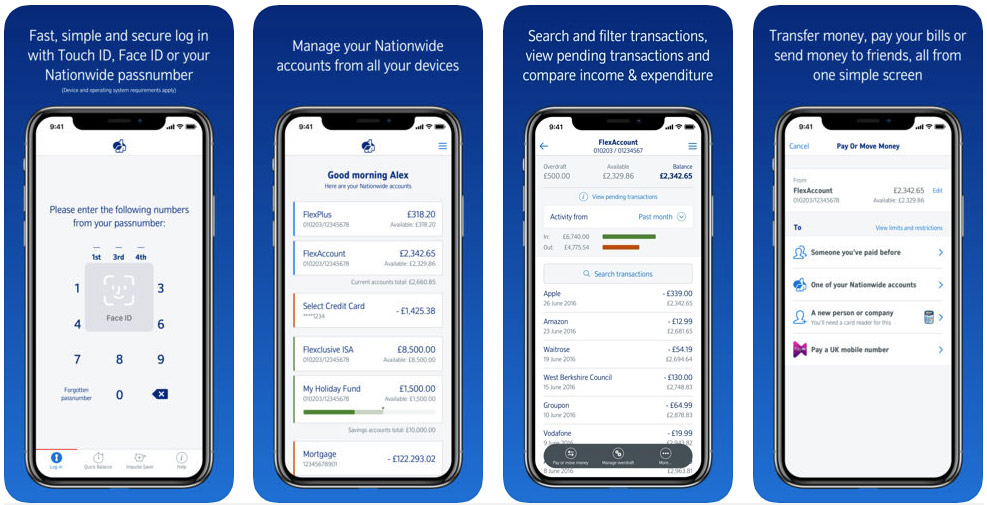
The Nationwide app uses Face ID and passive biometrics to secure a user's account.
According to a US corporation IBM study, in 2018 67% of consumers had a positive attitude to the biometrics authentication, and 87% were willing to use it in the future.
Two years earlier, the company had announced plans to use passive biometrics to combat banking fraud. In 2016, the IT giant started developing its own project to protect digital banking, offering to analyze customer behavior using machine learning. This technology allows you to understand in real time how users interact with banks' websites.
IBM development is built on the work of three complementary elements:
Every time a bank client tries to access financial services online, his gestures are compared with the model that is recorded in the database. Thus, banks will be able to timely record an attempt of unauthorized access to accounts.
Payment protection from Mastercard. In 2017, the Mastercard payment system acquired NuData Security to prevent fraud. NuData Security's product, NuDetect, uses machine learning to analyze passive biometrics. The technology analyzes how the user is typing, holding the phone in order to anticipate and prevent fraudulent transactions on the Internet, including payments in the field of online commerce.
Usage example. In the spring of 2019, Mastercard signed a Memorandum of Understanding with mobile operator du (UAE) in order to test the effectiveness of the NuDetect solution. This solution is expected to help Mastercard create safer and more convenient payment methods for its users in the Middle East and Africa. Anthony Schiner, Chief Digital Lifestyle and Innovation Officer at du, said the partnership with Mastercard will further simplify the payment process for consumers across multiple channels, while maintaining a high level of security during transactions. Shiner also stressed that the mobile operator sees tremendous potential in NuDetect and looks forward to a long and fruitful cooperation.
Visa and passive biometrics. In the spring of 2019, the Visa payment system signed an agreement with the IT company Fortress Identity to integrate additional protection for Visa cards for users in Latin America and the Caribbean. For these purposes, the program developed by Fortress Identity will use voice recognition technology and passive biometrics.
We want Visa cardholders to have complete confidence that their funds and personal information are safe wherever they use their Visa cards.
Fortress Identity is also said to be partnering with Visa partners including payment provider YellowPepper, banking services provider NovoPayment and HST, an international EMV standard provider. Chiarini also highlighted the importance of using multi-factor authentication at the Visa Latin America and Caribbean Summit in March 2019.
Multi-factor user authentication is critical in today's interconnected commerce space, and authenticating users trying to access the network is key to reducing many types of fraud, including chargebacks.
NuDetect will allow online banking and the Privat24 mobile application to validate customers by their unique behavior when interacting with devices and applications. The solution analyzes hundreds of signals, including device characteristics, passive biometric and behavioral metrics. Then - compares them with the way the user behaved in the past.
According to Natalia Kangina, head of digital products at Mastercard Europe SA in Ukraine, using machine learning, the NuDetect platform creates a client profile that collects more than 300 of its unique properties. Based on these parameters, the platform determines in real time whether the user is a real customer or a fraud.
Note. PaySpace Magazine clarified with Bank at what stage is the launch of the project using passive biometrics. As comments arrive, we will add them to the material.
Visa. At the beginning of the year, Visa announced a gradual transition to the 3D Secure 2.0 standard , which implies the refusal to authorize all transactions and the use of selective identification of suspicious customers, including using biometrics. According to Kristina Dorosh, Senior Director of the Key Products Department in the CIS and Southeastern Europe, after the implementation of the updated standard, it will be necessary to verify only those transactions that, according to various criteria (amount, location, etc.), are out of the normal pattern. According to Dorosh, 3D Secure 2.0 should go into effect in 2020.
Behavioral biometrics: the most effective solutions and in the world.
Several years ago, the American information platform TeleSign published a study according to which two-factor authentication and behavioral (or passive) biometrics will soon completely replace passwords. For example, in 2016, 9 out of 10 companies reported that behavioral biometrics would be a huge benefit to their security systems. 54% of companies expressed their intention to implement this method of protection in the future. The PaySpace Magazine editors found out which financial companies have taken up the implementation of this technology in Ukraine and the world.
What is behavioral biometrics
Passive biometrics even analyzes how you hold your smartphone.Behavioral biometrics is a human recognition system that identifies a person by dynamic (behavioral) characteristics. Behavioral characteristics include handwriting and signature dynamics, voice and speech rhythm, gesture recognition, electronic device usage (typing speed, holding a smartphone or tablet), and even gait. Behavioral biometrics are also referred to as passive biometrics.
Behavioral biometrics and the world's best solutions
Digital identification for financial companies. In 2014, the Israeli company BioCatch invested $ 10 million in expanding a biometric platform that collects and analyzes hundreds of behavioral signals and is used by banks to identify suspicious user behavior on the Internet.Today, the company offers customers a patented technology based on artificial intelligence, which in real time allows you to establish and confirm the identity of the client (in particular, by analyzing how the user holds the smartphone and how it controls it) to confirm the transaction or cancel it if signs of fraud are detected. The program also uses a built-in privacy algorithm to keep user data safe.

BioCatch analyzes the user's hand size and how he holds the device.
The BioCatch product is currently used by the Brazilian banking company Itaú Unibanco, the British large commercial bank NatWest and the American financial company American Express.
Usage example. One of BioCatch's largest clients, the Royal Bank of Scotland (RBS), is currently using the company's service to protect more than 18 million corporate and individual accounts. When logging into an RBS account, the program records more than 2 thousand interactive gestures of the client - from the angle at which he holds the mobile device to the fingers he uses to control the application. If the client uses the desktop version of the application, the program reads the speed of typing on the keyboard and pressing the mouse keys.
In 2018, the program recorded unusual activity coming from the account of one wealthy client. After authenticating, the visitor used the mouse scroll wheel - something the client had never done before. The user then entered the numbers at the top of the keyboard instead of the side they usually used. RBS blocked access to funds in the customer's account, which later turned out to be hacked.
According to Kevin Hanley, director of innovation at RBS, thanks to the development from BioCatch, the bank was able to prevent a fraudster from stealing a seven-figure amount from the client's account.
Criticism of passive biometrics. As noted by The New York Times, despite the successful prevention of fraud by the Royal Bank of Scotland, this case is perceived ambiguously. In particular, due to the fact that the user's behavior is not always constant, since the same person can behave differently in different situations due to fatigue, drunkenness, feeling unwell, or banal rush. The journalists also emphasized that a person can enter text in different ways, being behind a computer screen in the office and lying on the couch at home.
UnifyID: passive biometrics as a mobile app.In 2016, the American company UnifyID introduced a new system that analyzes user behavior and habits, his biometric characteristics, typing rhythm, location and movement, as well as how he interacts with different devices. Using machine learning, the program analyzes the information received, identifying the identity of the user. As the representatives of the company commented, the decision to resort to innovative solutions in the field of personal identification was made due to the unreliability of the systems available on the market.

UnifyID analyzes biometric data of the user in real time.
The new system works as follows: the user needs to install a browser extension and a mobile application on his smartphone, which will study and eventually recognize it by the above characteristics.
The developers also took into account the fact that at first the user and the system will not be "familiar enough" for the program to instantly identify itself. To do this, at the initial stages of "dating", she will send a call to the user's phone, who will need to put his finger on the fingerprint scanner to confirm his identity.
Consumer data collected by the system is encrypted on the local device. Currently, the UnifyID product is available for iOS 10+ and Android 5.0+ users.
Banking application with passive biometrics. In 2016, the Nationwide Building Society, a British financial services provider, took over the development of a mobile banking application using behavioral biometrics . Tech companies BehavioSec and Unisys also took part in the project.
The Nationwide banking app, which is available for iOS and Android users, evaluates the user's actions, in particular, how he interacts with a smartphone or tablet. Passive biometrics are used to authenticate the consumer when making payments made in the app as an additional layer of protection.
In 2019, Nationwide announced that it would invest in Scaled Insights, a company that uses behavioral AI to analyze people's speech to communicate with users in their preferred language.

The Nationwide app uses Face ID and passive biometrics to secure a user's account.
According to a US corporation IBM study, in 2018 67% of consumers had a positive attitude to the biometrics authentication, and 87% were willing to use it in the future.
Two years earlier, the company had announced plans to use passive biometrics to combat banking fraud. In 2016, the IT giant started developing its own project to protect digital banking, offering to analyze customer behavior using machine learning. This technology allows you to understand in real time how users interact with banks' websites.
IBM development is built on the work of three complementary elements:
- fraud detection and analysis of user behavior
- continuous authentication
- mobile multi-factor authentication
Every time a bank client tries to access financial services online, his gestures are compared with the model that is recorded in the database. Thus, banks will be able to timely record an attempt of unauthorized access to accounts.
Payment protection from Mastercard. In 2017, the Mastercard payment system acquired NuData Security to prevent fraud. NuData Security's product, NuDetect, uses machine learning to analyze passive biometrics. The technology analyzes how the user is typing, holding the phone in order to anticipate and prevent fraudulent transactions on the Internet, including payments in the field of online commerce.
Usage example. In the spring of 2019, Mastercard signed a Memorandum of Understanding with mobile operator du (UAE) in order to test the effectiveness of the NuDetect solution. This solution is expected to help Mastercard create safer and more convenient payment methods for its users in the Middle East and Africa. Anthony Schiner, Chief Digital Lifestyle and Innovation Officer at du, said the partnership with Mastercard will further simplify the payment process for consumers across multiple channels, while maintaining a high level of security during transactions. Shiner also stressed that the mobile operator sees tremendous potential in NuDetect and looks forward to a long and fruitful cooperation.
Visa and passive biometrics. In the spring of 2019, the Visa payment system signed an agreement with the IT company Fortress Identity to integrate additional protection for Visa cards for users in Latin America and the Caribbean. For these purposes, the program developed by Fortress Identity will use voice recognition technology and passive biometrics.
We want Visa cardholders to have complete confidence that their funds and personal information are safe wherever they use their Visa cards.
Fortress Identity is also said to be partnering with Visa partners including payment provider YellowPepper, banking services provider NovoPayment and HST, an international EMV standard provider. Chiarini also highlighted the importance of using multi-factor authentication at the Visa Latin America and Caribbean Summit in March 2019.
Multi-factor user authentication is critical in today's interconnected commerce space, and authenticating users trying to access the network is key to reducing many types of fraud, including chargebacks.
Behavioral biometrics
Mastercard and PrivatBank project. The companies plan to introduce the first in Ukraine authentication based on behavioral biometrics. The new solution is provided by NuDetect, a transparent user verification platform from NuData, a Mastercard company. The project is planned to be completed by the end of 2019.NuDetect will allow online banking and the Privat24 mobile application to validate customers by their unique behavior when interacting with devices and applications. The solution analyzes hundreds of signals, including device characteristics, passive biometric and behavioral metrics. Then - compares them with the way the user behaved in the past.
According to Natalia Kangina, head of digital products at Mastercard Europe SA in Ukraine, using machine learning, the NuDetect platform creates a client profile that collects more than 300 of its unique properties. Based on these parameters, the platform determines in real time whether the user is a real customer or a fraud.
Note. PaySpace Magazine clarified with Bank at what stage is the launch of the project using passive biometrics. As comments arrive, we will add them to the material.
Visa. At the beginning of the year, Visa announced a gradual transition to the 3D Secure 2.0 standard , which implies the refusal to authorize all transactions and the use of selective identification of suspicious customers, including using biometrics. According to Kristina Dorosh, Senior Director of the Key Products Department in the CIS and Southeastern Europe, after the implementation of the updated standard, it will be necessary to verify only those transactions that, according to various criteria (amount, location, etc.), are out of the normal pattern. According to Dorosh, 3D Secure 2.0 should go into effect in 2020.
