BadB
Professional
- Messages
- 2,415
- Reaction score
- 2,368
- Points
- 113
Hello young hacker, in this article we will look at such a sub-area of hacking as malware analysis.
In this article, you will find out:
Traffic analysis.
Perhaps one of the most important things when analyzing a virus. And so, to analyze outgoing traffic, special programs are used - sniffers. The most popular ones are:
Consider what we can learn about the virus, according to its requests.
Open our sniffer, in my case it's Fiddler:
Program interface.
We launch the virus, then see what requests were sent:
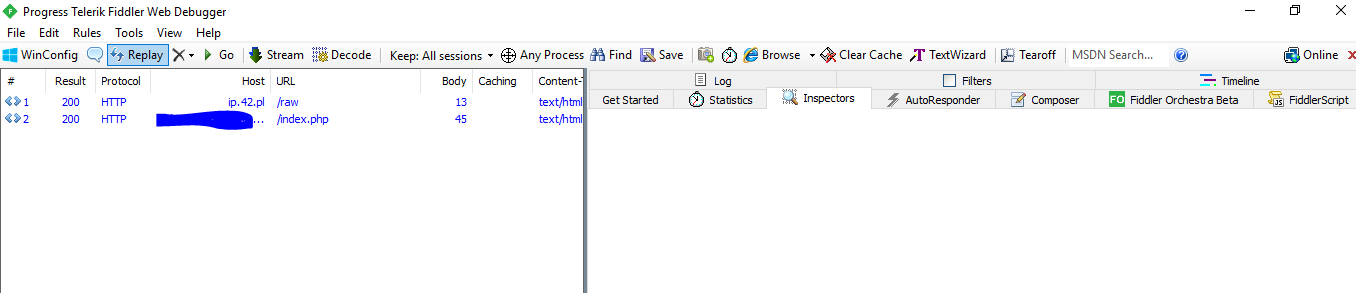
Let's analyze them. The first request flew to this site: http://ip.42.pl/raw
When you go to it, your external IP will appear, the malware uses this site to parse your IP user.
The second request went to the domain, and the following was shown when navigating to it:
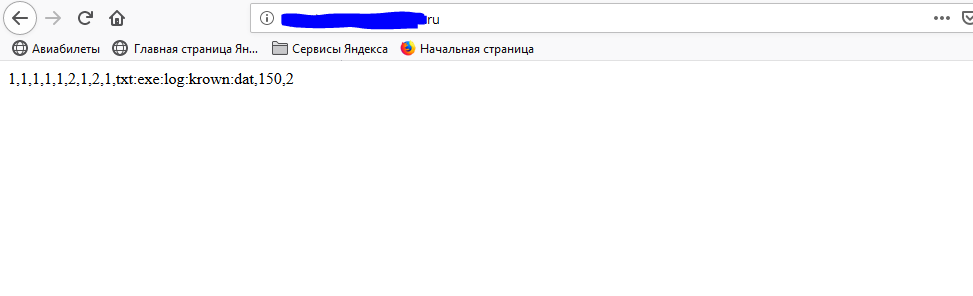
All these numbers are needed to parse software functions. Let me give you an example. When the software made a request and copied the numbers, a check occurs: If the first digit == 1, then the software needs to steal the logs; passwords, as an example in pseudocode, but I think you understand.
When you received the domain of the panel, you can also analyze the panel itself for vulnerabilities, throw brute force, spizd the logs. For malware-hunters, the panel is a very important clue, because if the panel is on a non-bulletproof hosting, they can send a request to the administration, asking them to provide all the information about the owner of this domain. Well, there is increasing.
Of course, malware developers should understand that sooner or later, their brainchild will begin to be studied, but if you thought that there was no protection from traffic analysis, you are grossly mistaken. For example, I made Anti-Analysis in my software, and in one of the methods I simply checked the running processes, and if there was a sniffer process among them, the software self-destructed, something like that.
System behavior.
To track the creation of files, folders, register operations, the Process Monitor program is most often used.

Program interface.
But before you start analyzing the system, you should set up the filters.
Go to the "Filter => Filter ..."

Add the required filter - Process Name, begins with, process_name, Include:

Instead of who is the name of your process.
We also add a filter to the Windows folder, this is necessary so that when the malware accesses any DLL, we do not have unnecessary entries.
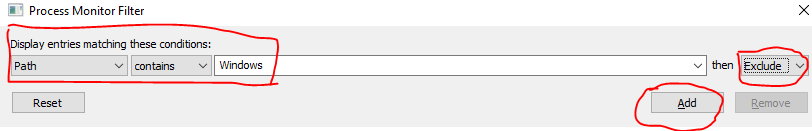
Now, in the main window, select what to track: Register activity, File system, Network traffic, Streams
Now everything is ready, let's start the analysis of the system with the keyboard shortcut: CTRL + E.
Next, we launch our virus and see the output
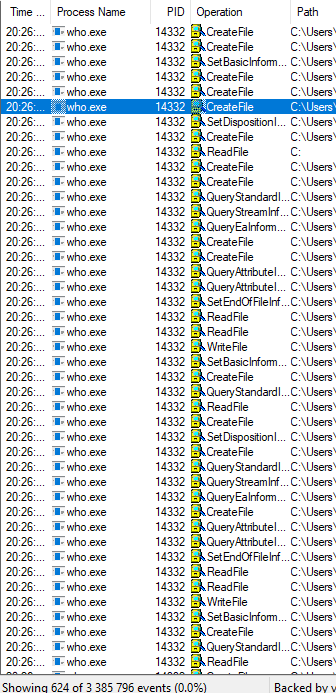
Let's analyze some of the actions. The first thing the software does is create a folder in the Temp directory with the username and hide it:
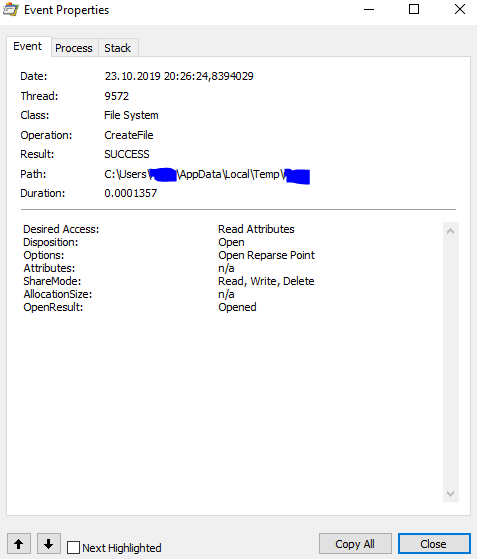
Creature
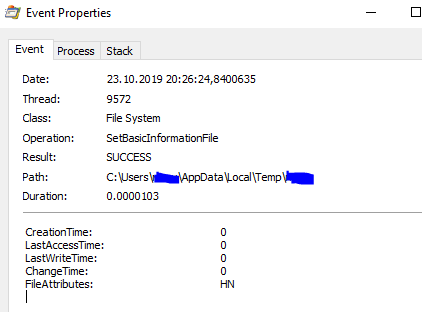
Hiding
Then it receives the paths to the database of files of the browser's chromium - Login Data, which contain logins and passwords, and also copies this file to a temporary directory

After that, it pulls out passwords, cookies, browser history from all databases and writes down files
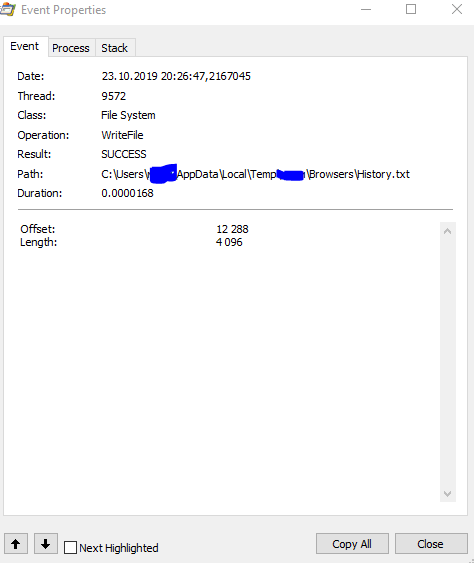
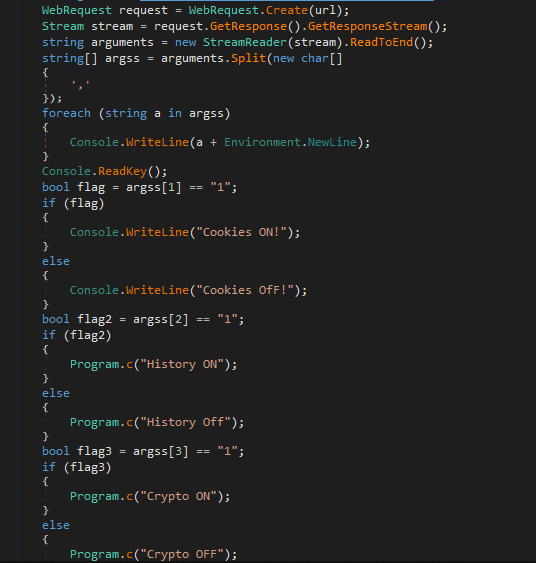
Well, further, it acts in the same way as other viruses of this type, collects files from the desktop, steam, telegram. Then it archives the folder and sends it to the domain that was in the traffic analysis.

This completes the analysis of the system, and the files created, move on to the next item.
Reverse engineering.
In this article, I will only touch the very basics of reverse .Net applications.
Tools.
For reverse, we need programs:
dnSpy - Disassembly tool, in simple terms, this utility will allow us to get all the code from the exe file.
DnSpy includes a decompiler, debugger and assembly editor. It can be easily extended by writing your own extension.
Let's get down to business, open dnSpy, and put our file there

And if the result turned out to be something like this, then you are lucky the virus is not obfuscated.
Well, method calls
Conclusion.
That's all, in this article we have only scratched the surface of malware analysis. If you are interested in this topic, then first I advise you to learn at least a couple of programming languages, so that afterwards you can understand what is happening in the code. Then master the reverse, practice deobfuscation, work with IDA Pro. That's all.
In this article, you will find out:
- How to intercept and analyze the traffic of a virus
- How to analyze the system for changes.
- How to study the malware code. Reverse engineering.
Traffic analysis.
Perhaps one of the most important things when analyzing a virus. And so, to analyze outgoing traffic, special programs are used - sniffers. The most popular ones are:
Consider what we can learn about the virus, according to its requests.
Open our sniffer, in my case it's Fiddler:

Program interface.
We launch the virus, then see what requests were sent:

Let's analyze them. The first request flew to this site: http://ip.42.pl/raw
When you go to it, your external IP will appear, the malware uses this site to parse your IP user.
The second request went to the domain, and the following was shown when navigating to it:

All these numbers are needed to parse software functions. Let me give you an example. When the software made a request and copied the numbers, a check occurs: If the first digit == 1, then the software needs to steal the logs; passwords, as an example in pseudocode, but I think you understand.
When you received the domain of the panel, you can also analyze the panel itself for vulnerabilities, throw brute force, spizd the logs. For malware-hunters, the panel is a very important clue, because if the panel is on a non-bulletproof hosting, they can send a request to the administration, asking them to provide all the information about the owner of this domain. Well, there is increasing.
Of course, malware developers should understand that sooner or later, their brainchild will begin to be studied, but if you thought that there was no protection from traffic analysis, you are grossly mistaken. For example, I made Anti-Analysis in my software, and in one of the methods I simply checked the running processes, and if there was a sniffer process among them, the software self-destructed, something like that.
System behavior.
To track the creation of files, folders, register operations, the Process Monitor program is most often used.

Program interface.
But before you start analyzing the system, you should set up the filters.
Go to the "Filter => Filter ..."

Add the required filter - Process Name, begins with, process_name, Include:

Instead of who is the name of your process.
We also add a filter to the Windows folder, this is necessary so that when the malware accesses any DLL, we do not have unnecessary entries.

Now, in the main window, select what to track: Register activity, File system, Network traffic, Streams

Now everything is ready, let's start the analysis of the system with the keyboard shortcut: CTRL + E.
Next, we launch our virus and see the output

Let's analyze some of the actions. The first thing the software does is create a folder in the Temp directory with the username and hide it:

Creature

Hiding
Then it receives the paths to the database of files of the browser's chromium - Login Data, which contain logins and passwords, and also copies this file to a temporary directory

After that, it pulls out passwords, cookies, browser history from all databases and writes down files

Well, further, it acts in the same way as other viruses of this type, collects files from the desktop, steam, telegram. Then it archives the folder and sends it to the domain that was in the traffic analysis.

This completes the analysis of the system, and the files created, move on to the next item.
Reverse engineering.
Reversing is akin to cracking, however, reversing is more often understood as restoring the source code of a program from an executable code, often code reversing may not even be associated with the program protection algorithm.Reverse engineering is a study of some finished device or program, as well as documentation for it in order to understand the principle of its operation; for example, to discover undocumented features (including software bookmarks), to modify or reproduce a device, program, or other object with similar functionality, but without direct copying.
In this article, I will only touch the very basics of reverse .Net applications.
Tools.
For reverse, we need programs:
- ExeInfoPE / RDG Packer Detector
- dnSpy

dnSpy - Disassembly tool, in simple terms, this utility will allow us to get all the code from the exe file.
DnSpy includes a decompiler, debugger and assembly editor. It can be easily extended by writing your own extension.
Let's get down to business, open dnSpy, and put our file there

And if the result turned out to be something like this, then you are lucky the virus is not obfuscated.
Obfuscation - bringing the source text or executable code of a program to a form that preserves its functionality, but complicates analysis, understanding of work algorithms and modification during decompilation

Well, method calls

Conclusion.
That's all, in this article we have only scratched the surface of malware analysis. If you are interested in this topic, then first I advise you to learn at least a couple of programming languages, so that afterwards you can understand what is happening in the code. Then master the reverse, practice deobfuscation, work with IDA Pro. That's all.

